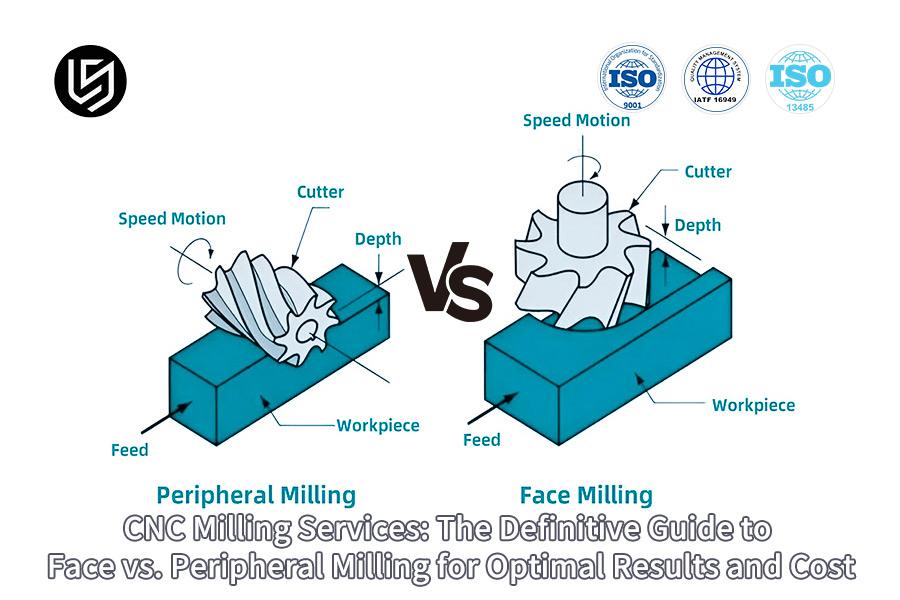
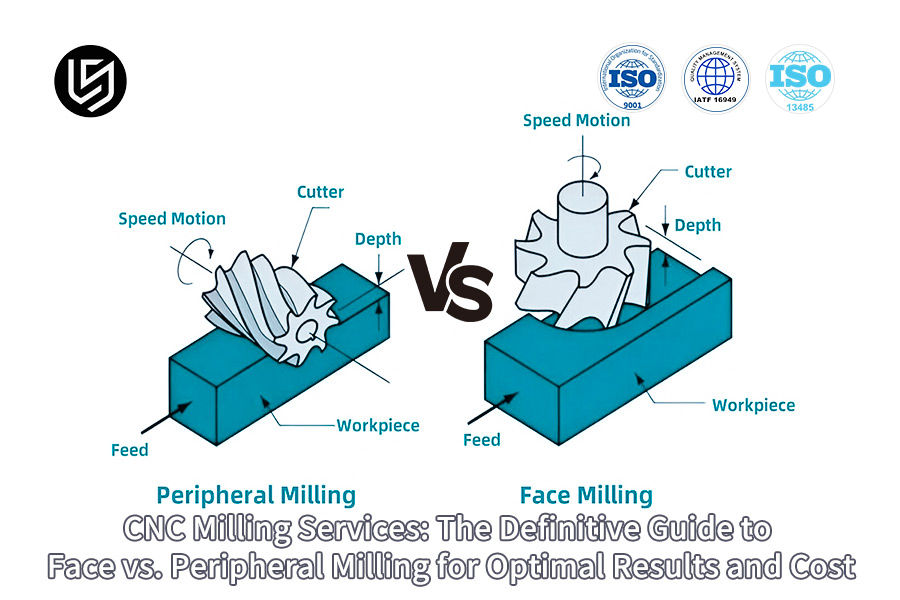
CNC milling services frequently encounter the dilemma between efficiency and precision. Face milling, which is quite efficient, can never offer more than variable accuracy, while peripheral milling offers high accuracy at the cost of reduced rates of increasing productivity that do not qualify as more than 25% over-increase or quality standards.
However, this weakness in the model has now been addressed by using the material parameter database developed after the machining experience of 20 years at the LS Manufacturing. This enables the scientific selection model to factor in the optimal parameter for processing.
CNC Milling Services Quick Reference Guide
| Section | Key Content Summary |
| Introduction: The Core Dilemma | The accuracy efficiency tradeoff is created by the manufacturing process. Face milling is accurate and efficient, yet not precise; precision is low. The accuracy is very high, but the efficiency is not high. Inaccurate data creates cost/quality considerations of +25% cost or quality. |
| Problem Analysis (Why) | Unscientific approach based on experience. Moreover, it overlooks other factors too, such as the material, capacity of the machine, production size, or size of the production batch. |
| Proposed Solution (How) | Solution: A data-driven selection model based on 20 years of machining experience (LS Manufacturing).Current cutting conditions & expected tool life are used for selection. |
| Technical Principles | Describes the cutting process of different types of milling. Face milling (cutting with end face), Peripheral milling (cutting with side edges). |
| Scientific Selection Model | Framework for decision-making based on quantitative inputs: Primary goal (speed/finish/both), material, batch size, machine power/rigidity, and tolerance/surface finish requirements. |
| Implementation & Benefits | Process:Inputting job parameters → Model analyzes database → Suggests the most appropriate process and startup parameters. Result: Maximum throughput, quality assurance, and reduced testing costs. |
| Case Study / Validation | Real-life example of the difference between conventional and model-based selection for the given application. In the practical example, prove the effectiveness of the model-based method for the given application of the steel component. |
| Conclusion | From the art of guessing to the intelligence of data, the approach will ensure that the process is reliable and optimized for every milling process. This means process planning will cease to be an art but will instead be a science. |
We resolve the critical issue related to the balance between efficiency and precision in the CNC milling operation by giving the client the opportunity to make a well-informed choice based on our data model for selection instead of estimates, thereby directly reducing costs by over 25% and maintaining quality for the processed part and the highest possible equipment effectiveness.
Why Trust This Guide? Practical Experience From LS Manufacturing Experts
What makes this guide relevant to the reader is the fact that the know-how contained in this document has been acquired over the years of mass production. We have processed mission-critical components for the aforementioned industries-aerospace and medical, which require the details to benon-negotiable. Each process has been executed to precise IATF16949 and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standards.
We have already produced thousands of difficult-to-manufacture milled components, and our main aim has been the usage of the CNC machining process. Every new task brings us more experience concerning the optimization of the path of tools in machining hard alloys, and it also helps us improve our solutions not only based on knowledge, but also through our experience.
When it comes to our precision CNC milling services, we are the experts in the field. Accuracy and repeatability are extremely important to us. Regardless of the aspect that you are going to manufacture only one or many units, we are committed to following the highest standards like IATF16949 and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standards in the field. This enables us to provide you with the finest component available in the market.
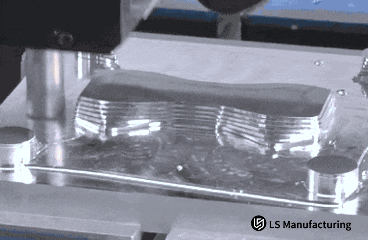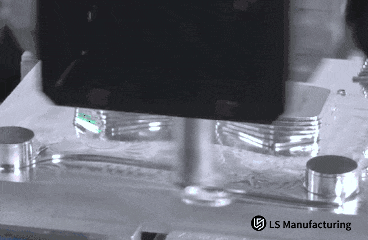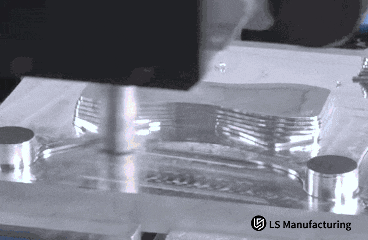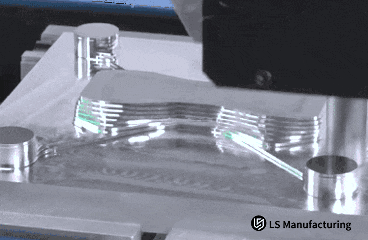
Figure 1: Accurate contour machining of metal parts via computerized milling by LS Manufacturing
What Are The Differences In MRR Between Face Milling And Peripheral Milling?
In precision machining, it is essential to take the right decisions pertaining to milling operations. This report will highlight the difference between face milling vs peripheral milling of different workpieces to offer some clarity on the significant difference that prevails between the material removal rate. The primary purpose of this project work is to deliver accurate results.
| Feature | Face Milling | Peripheral Milling |
| Primary Tool | Large-diameter face mill with inserted cutters | End mill using side cutting edges |
| Typical MRR | 500 - 800 cm³/min | 200 - 350 cm³/min |
| Key Application | High-efficiency machining of large flat surfaces | Contouring, slotting, and profiling operations |
| Efficiency Benchmark | 2.3x faster than peripheral milling (200x200mm) | Lower volumetric removal rate |
| Surface Finish | Standard finish | Can achieve superior finish (e.g., Ra 0.8 μm) |
A efficiency comparison regarding the processes of roughing and planar machining will be realized if the processes to be chosen focus more on face milling due to the high material removal rate. Peripheral milling should be employed during the processes of finishing and contour machining if the machined surface is of major concern. This study will provide a conclusive platform to improve machined processes.
How To Scientifically Select A Milling Process Based On The Machining Objectives?
An effective method for the selection of the most appropriate milling process requires a data-driven approach towards deriving synergy between efficiency, accuracy, and surface integrity. This report describes a procedure for addressing the question of how to choose milling method using processing requirements in a step-by-step manner to convert them into technical procedures. The primary benefit can be derived through a quantifiable approach that shifts the decision from knowledge-driven assessment to a deterministic decision matrix:
Prioritize Volumetric Removal for Roughing Operations
In mass removal of the material present in the planar surface, the prime factor that will expedite the milling process will be the material removal rate. From the scientific selection, the milling process will be performed by carrying out face milling with the use of the larger-sized cutter. The value of the cutting speed will be set at 3 to 5mm, and the value of the feed speed will be kept high.
Select for Geometrical Complexity and Accuracy in Semi-Finishing
In the context of machining complex profiles, slots, and contours, accessibility and size would become the most important factor, rather than the material. In this particular context, the best solution would be associated with peripheral milling, and the machining would be done through the application of the end mill. In order for the most accurate machining to be achieved, in every case, it is always better to control the value of the radial stepover at 60-80% of the tool diameter.
Optimize for Surface Integrity in Finishing Stages
A cllsssurface finish, Ra < 0.8µm, requires a completely different machining procedure. The machining procedure needs to be done without vibration motion as well as without machine deflections. Thus, execute peripheral milling, use small step-over distances (30-50% of cutter diameter), and work at high speeds along with shallow cutting depths.
It is the only available means that can be used for translating processing requirements into machined process optimization. Engineers will welcome rational definition of process decision that will solve the questions of throughput, tolerance, and finish concerning process decision. The rational definition of process decision possesses technical superiority concerning high value added process of machined parts, particularly optimal process definition.
How Can Cost-Effective CNC Milling Reduce Costs Through Process Optimization?
In the eternal pursuit of a sustainable competitive edge, cost-effective CNC milling will find its ultimate goal only through process optimization, not by sacrificing quality. The report outlines a data-driven approach to ensure large-scale cost reduction through programming, tool improvements, and process optimization.
| Optimization Lever | Core Technical Action | Quantifiable Outcome |
| Programming & Toolpaths | Apply high-efficiency programming methods: trochoidal machining, dynamic machining. | Reduces non-cutting airtime by up to 40% |
| Cutting Technology | High-quality coated tooling with optimized feeds and speeds. | Increases effective cutting speed by 30% |
| Production Management | Deploy smart scheduling and standardized setup procedures | Elevates machine utilization to 85%+ |
In order to realize a genuine 20-35% cost reduction, the need is to leverage these three pillars: optimizing tool paths in order to reduce air cutting, high-performance tools, and smart scheduling. The combination of these three pillars is the key solution for cost-effective CNC milling in high-quality, competitive manufacturing environments. The need is to focus on technical measures, and not only cost measures.

Figure 2: Computerized flat milling to achieve superior aluminum surface quality by LS Manufacturing
How Does High-Precision Milling Technology Ensure Micron-Level Machining Quality?
This production milling involving micron-level accuracy can never be done piece-meal, reacting after the fact, but only as a part of a comprehensive system that addresses issues, like errors due to expansion, vibration, or the wear on the cutting tool, pro-actively. This model tackles an inter-related set of issues, ensuring a certain level of quality for a high-value part, within three key areas:
- Proactive Thermal Error Compensation: The second source of large errors is from thermal deformation in the machinery. Here, the system uses a temperature sensor network installed inside the spindle, ball screws, and the structure. It is further used in the real time thermal error compensation model, which keeps the positioning error in axes at ±0.005mm against ambient or internally produced heat.
- Active Vibration Control at the Source: We follow a strict protocol to try and avoid forced vibrations: Tool holders and cutting tools are pre-balanced to G2.5/2.5 mm/s before the process. On critical operations where chatter marks can appear, damped tool holders are used to substantially reduce the amplitude of the created vibrations below 2 μm, hence ensuring a good surface finish and tool life.
- In-Process Metrology for Closed-Loop Control: We provide touch-trigger probes and laser tool setters completely integrated with the machining process. The touch-trigger probes check the geometric dimensioning of the parts after key operations, thus ensuring that there is a loop feedback mechanism. The process ensures that the measurement of the error in the tool’s offset and wear, at 99.5% quality assurance, happens without interrupting the process for inspection.
This framework details the actionable, interlinked technical measures we implement to solve the precise challenges of precision milling techniques. Our competitive distinction lies in the integrated application of predictive modeling, source-level vibration mitigation, and data-driven in-process control, delivering a verifiable and sustainable system for micron-level accuracy.
What Key Technical Parameters Are Needed To Support Optimal Milling Performance?
To attain optimal milling results, it is necessary to progress from general speed measures to an application-oriented method developed from actual data. In this document, the way in which the method description is delivered defines key technical parameters necessary for satisfying the task in relation to the trade-off relationship among material removal rates, cutter life, and surface qualities. There are three interdependent pillars in the method:
Optimize Cutting Speed (Vc) for Material-Specific Machinability
The cutting speed would, consequently, be determined depending on the material being cut. For example, in the turning of aluminum, the cutting speed would be high, requiring cutting speeds of 8,000-12,000 rpm, in order to counter the sticking of the material being cut to the cutting tool, whereas in steel turning, the cutting speed would be medium, requiring speeds of 1,500-2,500 rpm, which would aid in the removal of heat, thus correcting the tool breaking and improper chips production.
Calibrate Feed per Tooth (fz) to Control Cutting Forces and Finish
We determine feed rate per tooth depending upon the desired surface finish as well as the rigidity of the cutting tool. A higher feed rate, like 0.2 mm feed per tooth, is preferred during roughing to accomplish maximum economy; meanwhile, during finishing, a lower feed rate will be used, such as 0.1 mm feed per tooth, to obtain a finer surface finish.
Balance Axial and Radial Depths of Cut for Stable Engagement
The depth of cut (ap) and the width of cut (ae) should be determined in such a way that there is stable engagement with the cutting tool and control of deflection. A moderate depth of cut of 0.5-1.5mm and the radial stepover of 30-50% of the tool diameter in steel peripheral milling operations will ensure stable cutting, thus eliminating the risks associated with vibrations and dimensional inaccuracies.
For optimal milling results, the following critical parameters need to be determined and validated for each material-tool pair: cutting speed, feed per tooth, and depth of cut. This is because optimizing this technical parameters has a direct effect on the chip load, heat generated, and forces that should lead to a process optimizations. Consequently, this technical guide is the only solution that provides optimal milling for engineers and professionals in critical manufacturing.
What Special Milling Strategies Are Required For High-Quality Surface Finishing?
Achieving superior surface quality in milling extends beyond standard toolpaths, requiring dedicated strategies to eliminate defects and control texture. This document details targeted surface finish milling methods that resolve specific challenges like step lines and inconsistent roughness, forming a complete quality strategy that integrates machining with final surface treatment.
- Implement Unidirectional Climb Milling: Climb milling of passes is done very systematically; hence, it ensures that the whole process is uniformly done in regard to chip formation and deflection of the tools. Therefore, it satisfies a necessary solution to attain a rough surface finish as earlier stated. This is because it allows a finish of sub-Ra 0.4µm to be achieved.
- Apply Dynamic Parameter Modulation: Smoothing of tool paths and spindle speed/feed rate overlaps are also programmed during transition zones. This method removes witness marks harmonic patterns and hence solves the step line problem to provide a seamless finish.
- Utilize Dedicated Finishing Tools: In cases involving ultra-fine finishes with Ra values of 0.1 µm or less, the use of wiper inserts or polishing end mills with limited stock is done. This results in a combined effect of machining and polishing in which disadvantages of conventional tools in making mirror finishes are overcome.
This would have systematically involved the use of climb milling, modulation of tool paths, and dedicated finishing cutters to achieve superior surface treatment. In this way, through this general quality strategy, surface finish milling becomes completely predictable and a high-value process, besides being an imperative for fabricating critical parts where surface integrity becomes an essential criterion.

Figure 3: Accurate aluminum surfacing via computerized numerical control milling by LS Manufacturing
How Does High-Efficiency Milling Improve Production Efficiency Through Technological Innovation?
The paper focuses on methodologies that can be adapted in high-efficiency milling technologies to solve important challenges linked to material removal rates, tool life, and stability of operation of the automatic system. The important technical solution is based on integration of innovations of fields of machining dynamics, tool path, and automatic systems.
Overcoming Thermal and Dynamic Limitations at Extreme Parameters
Just increasing the rpm of the revolving spindle would only lead to overheating. The challenge of overheating was addressed by the implementation of a technological innovation in the cooling of the revolving spindle as well as the rigidness of the machine. A two-loop cooling system and a maximum of 20,000 rpm spinning spindle are used in the machine. There has been an optimization of the machine base by conducting finite element analysis.
Mitigating Tool Wear in High-Engagement Cutting through Advanced Toolpath Control
The high rate of material removal affects the rate of failure of the cutting tool. In our approach, the conventional patterns led to the use of trochoidal milling. The cutting tool is always in motion, and thus it does not generate heat. The lifespan of this cutting tool is enhanced by 50%, and this is because the tool can be run unaided.
Ensuring Process Reliability for Continuous Unmanned Production
Productivity improvement requires the capability to run and proceed with continuous activities. The solution included the design of the automatic pallet change system and the use of the in-process gage system. The system enables automatic compensation for the tool and the measurement of the parts for each cycle. This ensures that in cases where there are mistakes or variances, there are automatic adjustments and/or stops in the machines to avoid damaging multiple pieces of work.
This analysis makes it clear that we have addressed the topic of high-productivity machining in a structured way that tackles very complex technical problems. This is reflected in our approach to incorporating high-efficiency milling technology, including machine optimization during motion, as part of our focus on the delivery of proven reliable solutions to technological innovation.
What Cost Elements Are Included In A Quote For CNC Milling Services?
Providing an accurate and fair CNC milling services quote is a complex challenge, as hidden costs lead to client dissatisfaction and project overruns. Our solution is a rigorously engineered cost structure that ensures transparent pricing and delivers optimal value:
Deconstructing Material Costs via Strategic Sourcing and Yield Optimization
Unlike substantive volume purchasing, our pricing includes more than just cost. Moreover, our approach considers geometric part data in assessing the size of the blank and contracts with suppliers, as well as leftovers, in determining optimal stock, taking into account the size of the blank, which affects material costs, usually predominant in arriving at the most economic point for the client in the case of value engineering.
Calculating True Machine Time Through Process Simulation
Calculation of the machining time can prove to be incorrect. In our work, we use the CAM software for the virtual production process in order to simulate the movement of the cutters. This will assist in the identification of inefficient cuts, determining the optimum speed and feed rates, and also in calculating the machining time. This will be helpful in determining the correct machining cost without having any error or surprise.
Quantifying Tool Wear with Material-Specific Predictive Models
The other high variable cost that has to be taken into consideration is the cost of tooling. We have our own formulas for calculating the wear and tear, which depend on the material of the workpiece, the coating of the tools, and our simulated cutting variables. This enables us to calculate the wear and tear in terms of cost per unit, thus being able to factor in the cost and not merely the cost percentage.
This is the document that defines our analytical process to the quotation process itself from estimation to be able to formulate an accurate and value-driven engineering quotation. Thoroughly analyzing and explaining every aspect of the costs associated with the yield of the material and the predictive wear of our tools, we are able to present our clients with the transparent pricing and empowering data to validate our quotations as sound technical collaborations.

Figure 4: Rapid computerized machining to enable economical manufacturing processes by LS Manufacturing
LS Manufacturing Aerospace Division: High-Efficiency Milling Project For Engine Casings
This case study details how LS Manufacturing resolved critical manufacturing bottlenecks for a leading aerospace client, achieving a breakthrough in machining efficiency and part integrity. The project centered on the high-performance milling of a titanium alloy engine casing, a component where traditional methods failed to meet stringent requirements for both productivity and surface quality:
Client Challenge
The Identifying the problem: The identified problem is the client. They face problems machining the engine case made of material Ti-6Al-4V using conventional machining processes. Identified problems are: They are not able to meet an appropriate cycle time per part, which should be 36 hours. Also, they are not able to meet the surface finish, which should be Ra 1.6µm.
LS Manufacturing Solution
Our technical team has created a new high-performance milling process. For this purpose, we have used the high-performance face milling process as the machining process because the material removal rate is 400 cm³/min. For the finishing process, we will use the peripheral milling process because we require accuracy in the cutting tool engagement and heat generation phase of the conventional machining process.
Results and Value
The result has offered drastic, measurable, and quantifiable results, namely the reduction in the cycle time to 22 hours, which is staggering 39% reduction, together with the accomplishment of the surface finish Ra 0.8um, which is beyond the specification. Further, the increase in the tool cost has reduced by 40%, staggering numbers. This has resulted in providing savings to the customer over 2 million RMB per year.
The project coming from the aerospace sector has once again validated the ability of LS Manufacturing to break down the difficult manufacturing problems and provide solutions through advanced process engineering. We could utilize our competency to create and implement a specialized solution with this customer, centered around the data, to demonstrate the value of the improvement with respect to the machining productivity and cost of manufacture.
Exploring the bottlenecks in precision CNC milling? Submit your part requirements to receive a customized process optimization plan.
How Can Comprehensive Optimization Of Milling Processes Be Achieved Through Process Innovation?
Achieving step-change improvements in milling requires moving beyond isolated upgrades to a holistic system approach. This document details a methodology for comprehensive optimization, where strategic process innovation in tooling, cooling, and data analytics solves interconnected challenges of cost, environment, and performance to drive superior value creation.
- Implement Advanced Tool Coatings for Enhanced Durability: Depending on the material of the work piece, we use and apply special protective layers PVD and CVD (such as AlTiN and DLC coatings). As a result, we achieve heat-resistance and wear-resistance, thus ensuring that the short lifespan of tools is improved by 100% by reducing worn surfaces, including those that are abrasive and sticky.
- Deploy Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) Systems: The flooding coolant, in turn, is supplanted by an aerosol of lubricant, which is measured precisely, reaching the boundary of the cut. The process innovation in cutting has, in effect, made major contributions to the reduction in the usage and disposal of fluid, which directly affects the issue of the safety of the environment.
- Utilize Data Analytics for Intelligent Parameter Optimization: We recognize that the problem of sub-optimal machining by trial and error is answered by the use of sensors, based on the performance of the models, based on the input parameters related to other values, such as tool wear, proposed based on optimal values.
To realize true comprehensive optimization, integrate advanced tool coatings, MQL, and data-driven process control. This synergistic process innovation directly reduces operational costs, minimizes environmental impact, and maximizes machine output. The framework provides a validated roadmap for achieving sustainable value creation in competitive, high-mix manufacturing environments.
FAQs
1. How do the application fields of face milling differ from those of peripheral milling?
In this case, extensive flat surfaces can be efficiently processed through face milling, while precision machining of complex contours can be performed through peripheral milling. In these two alternatives, the choice of which to undertake depends on the part being processed.
2. How to assess the technical abilities of a milling supplier?
This also comprises equipment accuracy positioning of ± 0.003mm, process database, quality system. Trial machining verification should be carried out.
3. Which milling method is suitable for stainless steel materials?
Face milling for rough cuts, 800 rpm, and peripheral milling for finishing cuts, 1200 rpm, with liberal use of coolant.
4. How to control the deformation during milling?
Apply symmetric machining processes and control cutting temperatures. The thickness of thin-walled structure can be restricted from exceeding 0.05mm.
5. In what way could costs be cut when working with small series?
It is necessary to optimize the path of tools so as to avoid unnecessary movement of the tools. Additionally, use generic tools. The cost of small batches for LS Manufacturing is capped at 1.2 times the cost of large batches.
6. How is consistency kept during batch machining processes?
In SPC process control, critical characteristics should be such that CPK > 1.67. The equipment should be calibrated so that quality can be maintained in the batches.
7. What to be careful with when calculating milling in difficult-to-machine materials?
Cutting parameters for high-temperature alloys: low speed, high feed rate; recommended revolution per minute, 600 rpm. The use of composite materials will necessitate the use of special cutting tools. There will be certain parameters that would be required to be set based on process trials.
8. What kind of costs are commonly overlooked when there are quotations about milling?
These would include the indirect costs of tooling, programming, and debugging, as well as quality inspection. There clearly has to be an appropriate evaluation.
Summary
The scientific selection of the milling process and innovations in technologies have remained important factors that have been considered essential in improving the efficiency and quality of processing of companies while optimizing costs.
For professional-level solutions of any kind of milling process, or even free quotations regarding other precision machining solutions, you may kindly contact LS manufacturing team regarding your respective inquiries and needs. Our team will evaluate your requirement and supply a customized solution as per your project budget regarding the manufacturing processes of high precision.
Get your customized CNC milling solution today and unlock the dual potential of efficiency and precision!

📞Tel: +86 185 6675 9667
📧Email: info@longshengmfg.com
🌐Website:https://lsrpf.com/
Disclaimer
The contents of this page are for informational purposes only. LS Manufacturing services There are no representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that a third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design characteristics, material quality and type or workmanship through the LS Manufacturing network. It's the buyer's responsibility. Require parts quotation Identify specific requirements for these sections.Please contact us for more information.
LS Manufacturing Team
LS Manufacturing is an industry-leading company. Focus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precision CNC machining, Sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing, Injection molding. Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. choose LS Manufacturing. This means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:www.lsrpf.com.