In the foundry industry, is die casting superior to sand casting? It's a common but essentially erroneous question in the casting industry. The true answer is not "yes" or "no," but "There's no best process, only the most suitable one." Both of these old stand-by molding processes possess certain technical characteristics and economic justification. Die casting, utilizing metal molds and high pressure, records impressive production efficiency, better dimensional accuracy and surface finish, and is exceptionally well suited to making large quantities of highly detailed, thin-walled parts. Sand casting, employing throwaway sand molds, offers unmatched flexibility, extremely low mold cost, and virtually unlimited part size and material flexibility, and is the best choice for single pieces, small runs, and big castings.
Therefore, process selection is really a compromise of a wider scale in terms of some needs—such as production batch size, cost budget, part structure, performance requirement, and material. The following article systematically analyzes the fundamental differences and fields of application of these two processes to allow you to make the most rational choice. To save you time, here’s a quick overview of the core conclusions.
Die Casting vs. Sand Casting: Core Comparison Quick Reference Table
| Characteristics | Die Casting | Sand Casting |
| Production Efficiency | High, suitable for large-volume production | Low, suitable for small-volume or single-piece production |
| Unit Cost | High mold costs, extremely low unit costs for large-volume production | Very low mold costs, good economics for small-volume production |
| Part Size | Limited by equipment, suitable for small and medium-sized parts | Almost unlimited, capable of producing large parts |
| Precision/Surface | High precision, excellent surface quality | Low precision, rough surface quality |
| Material Compatibility | Primarily suitable for non-ferrous alloys (such as aluminum and zinc) | Suitable for almost all metals, including iron and steel |
The choice depends on what you most require:
- For medium to small components with high precision, high efficiency, and high volume, die casting is better;
- For a small batch, high flexi, big size, or cast steel/iron components, sand casting is better.
- It is neither absolutely to your advantage nor to your disadvantage; the sole point of discussion is whether it satisfies the project requirement.
Why Trust This Guide? LS Experts' Practical Experience
At LS, our personnel have hands-on experience of a couple of decades' standing in metal forming. We do not merely have deep knowledge of the technical aspects of an enormous quantity of processes such as die casting and sand casting but are also well conversant with cost-effectiveness and compromises in an extremely huge volume of industries and application fields. This means that you get dependable, in-market solutions and not theories.
Following actual operation, LS has been able to implement a general "sand casting pilot production + die casting mass production" mode for automotive component customers. During the process of making a product, low mold cost and high applicability of sand casting are taken to enable customers to quickly finish prototype verification and small batch test output with low investment. When the product is mature and served to support mass production, die casting will be used without shutdown. High efficiency and precision of die casting greatly decrease the cost of units and ensure consistent quality, overcoming the main difficulties of the overall development and mass production process successfully.
Die Casting vs. Sand Casting: Which Is King?
In foundries, "what's king, the die casting or sand casting" is an age-old question but one to which one cannot definitively say there is a winner. Practically speaking, no process has a clear-cut advantage when actual project requirements are considered—piece batch quantity, cost budget, material composition involved in process, piece complexity, these determine the most favorable process.
Die Casting
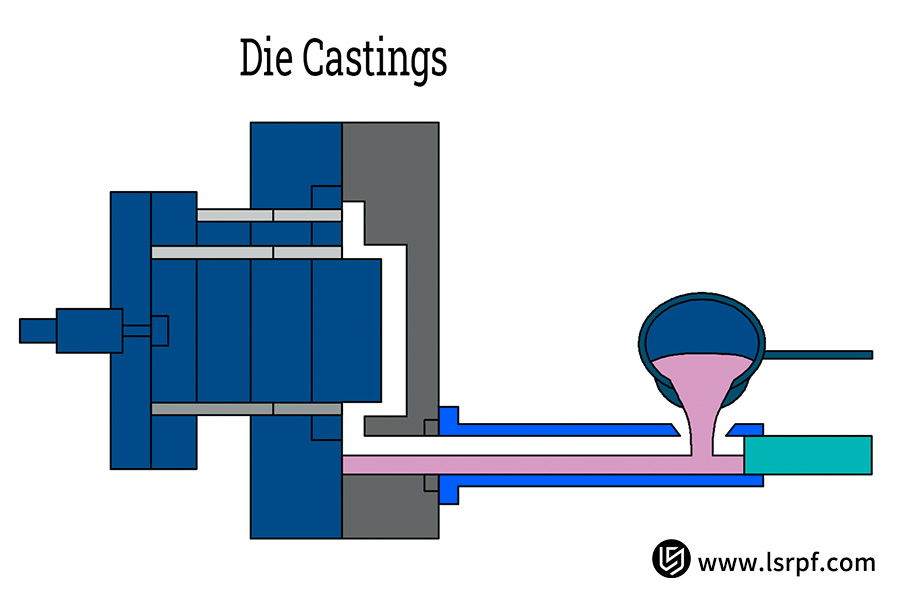
Die casting makes use of high pressure and high speed to inject liquid metal at a fast rate into a pre-fabricated reusable metal die (or "die"). It is solidified and cooled under pressure, and a metal casting of complex shape and high precision and fine finish is eventually achieved. High rate of production is a characteristic of die casting and is employed for bulk production. It gives a finished product of precise dimensions and fine surface finish.
Sand Casting
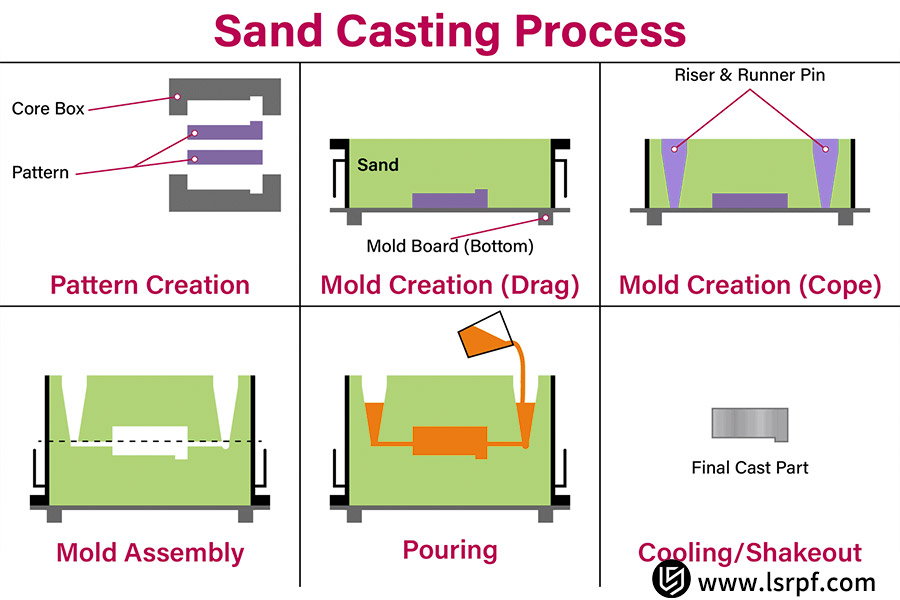
Sand casting, undoubtedly, has a throwaway sand mold, is slow and low-pressure casting, takes advantage of ease of moldability and mold softness to pour hot metal into mold, and crushes mold when metal has solidified to produce a desired casting. Although slower and more rough in surface, sand casting is extremely low-cost in mold and is extremely portable. It is perfect at producing large, complex, or low-volume output, and it has more material to offer.
- These two technologies are not alternatives but complements to one another.
- Being aware of their principles and natures will set us free from the stereotype of "which is better, which is worse" and enable us to select the most economical and efficient choice for individual applications.

Why Do High-volume Projects Prefer Die Casting?
In high-volume manufacturing projects, die casting is the preferred process due to its inherent advantages. This is largely due to its advantages in this area. So, what are the advantages and disadvantages of die casting? Let's explore these points.
1. Advantage of Die Casting:
Large volume buying favors die casting because it takes the lead in volume production. Die casting realizes record-breaking output efficiency through ramming molten metal into steel dies of ultimate precision at high speed and high pressure. Molds can be recycled at a rapid and easy rate, as well as the process being highly mechanized and cyclic in terms of seconds, and thus ideal for thousands and even millions unit buys.
This process is also guaranteed to provide fine dimensional accuracy and surface finish, and final products are of close tolerances and fine finish. To a large extent, these products can directly go into assemblies without further machining, and thus greatly lower the cost of units to be made. In addition, die casting is especially proficient at producing components of complex structure, thin-wall components, and slender shapes, fully satisfying the light weight and nearly integral need of contemporary products.
2. Limitations of Die Casting:
Of course, die casting is not without its limitations. It has the major limitation of requiring extremely high first mold cost and is not so efficient for low-volume batch work. It is mostly compatible with non-ferrous material like aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and their respective alloys but has low efficiency with ferrous ones like steel. Owing to the probability of gas entrapment when high-speed mold filling is involved, the die-cast components are generally found to contain poor internal density and poor toughness and are hence not compatible with structural components which are required to contain extreme strength, toughness, or impact resistance.
- In mass production, die casting's general benefit of economy, accuracy, and uniformity of output will surpass its disadvantage of high mold cost.
- When the mold cost is distributed over the amount of production, the unit cost of the piece is vastly competitive and actually the reason die casting is a requirement for a high amount of output.
In What Situations Is Sand Casting A More Sensible Choice?
Now that we understand the advantages of die casting for high-volume projects, when might sand casting be a wise choice? We'll analyze the advantages and limitations of sand casting to help you make the best decision.
1. Advantages of Sand Molds:
When prototyping off of small-batch production, mass-produced products, or specialty products, sand casting is usually the low-cost and prudent option. As its primary benefit is having an extremely low-cost mold, the mold is usually of resin, wood, or metal with fast reproduction cycles and low-cost pricing. This is relevant to prototyping, low-volume runs, or specialty one-run production without having to contend with the enormous startup cost risk of die casting.
More to the point, sand casting is near unlimited in part size or material selection. Machine bases for hundreds-of-ton machine tools, engine blocks, and applications where high melting point materials such as cast iron, cast steel, and copper alloys are necessary are no problem, and die casting can't even hope to match the task. Furthermore, since the metal cools more slowly in the sand mold, internal density of the casting is higher and has increased toughness and lower residual stress. Mechanically, its properties are generally superior to die castings and are well adapted to produce structural parts that will be subjected to excessive loading, impact resistance, etc.
2. Limitations of Sand Casting:
There are limitations to sand casting. Manufacturing is much more inefficient compared to die casting. Every single sand mold will be cast only once, and you have to do multiple molding and have a lengthy production cycle. In addition, the final castings have low dimensional accuracy and surface finish with draft angles and rough surfaces. The castings will have to undergo much cleaning and machining to achieve service specifications and that involves additional time and expense.
If you have to produce thick, large, low-production, or high-melting-temperature metal components, and toughness at the expense of surface finish is more important, then sand casting with its unmatched versatility, economy, and material ability is definitely the better option.
Beyond Cost And Output: What Other Key Factors Influence Your Decision?
Where cost and volume are certainly considerations in whether to select sand casting over die casting, more fundamental technical considerations are more frequently the reason for lasting success and truly dictate product performance, quality, and overall verification cycle time.
Part design complexity
The complexity of a part is an important point of consideration. When fine features are thin-walled, internally complex in geometrical features, or ribs in pitch proximity, then reinforcement die casting, due to its high fill pressure, will detail finer and a more complex shape. As a general rule, overall general size is more adaptable to sand casting, but its ability is limited for extremely fine features.
Post-processing requirements
Post-processing needs affect cost and lead time directly. Die castings are of favorable surface finish and dimensional accuracy and typically remain low in post-processing (deburring, e.g.) and can frequently be put together straightaway. Sand castings are of low surface finish and tight dimension tolerances and typically need to undergo large amounts of machining to gain final shape and accuracy, and lead to extra time and cost.
Mechanical performance requirements
Mechanical performance requirements are the top consideration in the selection. When your parts will experience heavy loading, impact, and fatigue (such as structural parts for heavy equipment), sand casting is the better choice. Its more gradual solidification rate creates the inner structure of the casting denser and isotropic and consequently more impact- and fatigue-resistant. Die castings, with the possibility of internal porosity, are lower in toughness and ductility.
Surface treatment options
Finally, finish surfaces that make up the final appearance are also defined according to the substrate. If high cosmetic quality plating, painting, or anodizing is being considered, the smooth, close surface that die casting offers is the perfect substrate. Porous, rough base that sand castings have may need special pre-treatment processes (grinding and sealing) for high cosmetic quality.
- Therefore, apart from cost and volume, your decision has to be a wholistic one based on design complexity, level of post-processing required, performance requirement, and surface finish.
- Drawing an inference requirement of such a "hidden technical language" will enable you to shift from such yes or no decision to making the optimum decision that actually addresses the requirements of the entire life of a product.
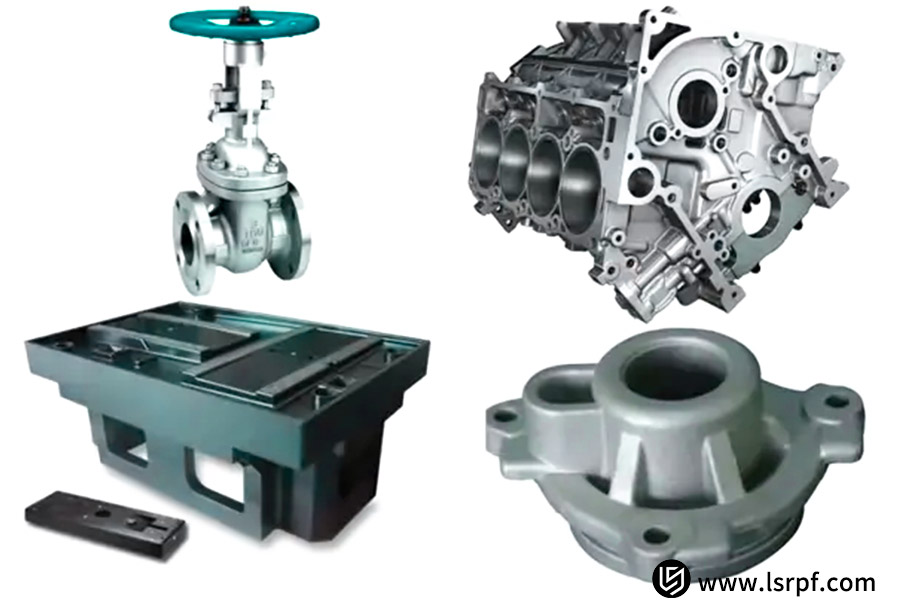

How Does LS Select The Optimal Casting Solution For Its Customers? An Automotive Part Manufacturing Case Study
1.Client Challenge:
One of the globe's leading auto makers was presented with a daunting challenge when creating a new model: how to cost-effectively and efficiently produce a high-end aluminum alloy engine bracket. Costs had to be reduced and turnaround times had to shorten while still providing consistent mechanical performance.
2. LS's Innovative Solution:
In light of this challenge, LS engineers did not recommend a lone process but instead suggested a phased, modular manufacturing process. For the first small-batch trial production and performance test phase of the project, LS suggested sand casting. Under this process, the client was able to produce working prototypes in a short lead time with low-cost tooling. Prototype, besides surviving bench test that confirmed the integrity of the structural design, also yielded important information to be used in subsequent design optimization.
3. Distinguished Achievements:
When the end product design was taken up for volume production, LS's solution enabled a smooth transition. We developed a high precision high-cavity die-casting mold for our customer, transforming the process to high-pressure die-casting. During the entire process conversion, the productivity of the process was substantially improved, registering a massive increase in the daily output capacity. Apart from that, with the high degree of die casting precision and low wasteage, the cost per piece was substantially lowered, addressing the customer's primary needs of cost reductions, process enhancements, and consistent supply.
- In LS's case study, the company truly tested out its value proposition of addressing customer needs across the entire product lifecycle. We do not offer a casting process alone;
- we offer a comprehensive solution of balancing competitiveness, adaptability, and consistency that definitely aids customers hurdle over massive barriers from R&D to volume production and produces a win-win outcome.
Which Process Is Best For My Design? Let LS Engineers Provide Professional Advice
If you are presented with the option of choosing between sand casting and die casting, do you take the cost, efficiency, and performance trade-offs into consideration? LS's experienced engineers are at your service to assist you in making the best decision.
- We provide no-cost Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis. Just send us a product design drawing or concept design, and our skilled process engineers will make a detailed evaluation from a manufacturability point of view, general cost, and final product performance.
- Not only do we identify the most favorable casting process accurately (die casting, sand casting, or otherwise), but also make design improvement suggestions actionable, such as suggesting an optimal location of the rib, draft angle maximization, or redistribution of wall thickness. This will benefit you to eliminate manufacturability risk and unnecessary cost from the onset.
Do not attempt to do it yourself. Reach out to LS engineers today and receive a tailored, expert process analysis and recommendations, putting your project on the right track from day one.
FAQs
1. Which is cheaper, die casting or sand casting?
Cost comparison should be taken into account with production volume. For small volumes (small series, e.g., below 100 pieces), sand casting is more cost-effective due to the disposable mold of sand, thus having practically no mold cost. For huge volumes (usually above 10,000 pieces), though there is a high mold cost involved in die casting, because of its much higher level of automation, having a short run, and much lower piece cost, it is more cost-effective in the overall scale. To determine the actual overall scale. calculation, volume of actual production must be taken into account.
2. Can I use die casting to produce large iron castings?
No. It is generally restricted to non-ferrous metals. It is limited by two constraints: Firstly, the molds are usually made of die steel and cannot withstand the high pouring temperatures of cast irons over 1200°C.; and, secondly, the die casting machines are restricted in size and will only generally take small and medium-sized parts. Big iron castings (such as engine blocks and machine tool bases) are always the Sand casting process's forte, since it is capable of using high-temperature-resistant sand moulds and has practically no limitation to the size of the component.
3. Which process produces stronger parts?
All processes contain specific strength characteristics. Sand castings solidify slowly and hence an isotropic and uniform microstructure is developed. Ductility and impact toughness are enhanced and are a result of such castings are broadly utilized in structural components and dynamically loaded. Under pressure, die castings are put to a mold and hence to a high surface level of hardness and precise dimension are achieved. But internal porosity and low ductility comparatively result from high cooling rate. Precise selection is relying on application mechanical properties.
4. How do I make the final decision?
The best method is to present product drawings and technical specs to an experienced manufacturer. For instance, at LS, we offer a complimentary manufacturing feasibility study. Your part design, batch specifications, performance requirements, and budget will be analyzed in detail in this important analysis, giving you the best process solution and design optimization recommendations to achieve the most cost-effective solution.
Summary
Neither is there an absolute superiority nor an inferiority of die casting to sand casting, nor vice versa, but just the specific application and project needs that make them valuable. Die casting has many areas of superiority in efficiency, accuracy, and finish and, consequently, is most appropriate for mass production. Sand casting has unique finish and detail capability, low startup cost, and better material adaptation capability and is unmatched in single piece, mass, and specialty alloy work. Good process selection is a question of in-depth product characteristic study, objective of the production, and overall cost, and not a comparison of the two processes.
As a dual-capable die casting and sand casting manufacturer, LS is customer-focused and provides objective, professional process advice. We not only assist your decision of the optimum molding process, but maximize cost savings and product competitiveness by design optimization and complete process support. To get the ultimate solution, just send a request for inquiry and receive a tailored proposal from LS engineers.
Upload your design drawings now and get an instant metal casting quote (metal casting), let LS be your strong backing in pursuit of ultimate metal casting precision!
📞Tel: +86 185 6675 9667
📧Email: info@longshengmfg.com
🌐Website:https://lsrpf.com/
Disclaimer
The contents of this page are for informational purposes only.LS seriesThere are no representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that a third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design characteristics, material quality and type or workmanship through the LS network. It's the buyer's responsibilityRequire parts quotationIdentify specific requirements for these sections.Please contact us for more information.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal manufacturing,3D printing,Injection molding,Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseLS technologyThis means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:www.lsrpf.com