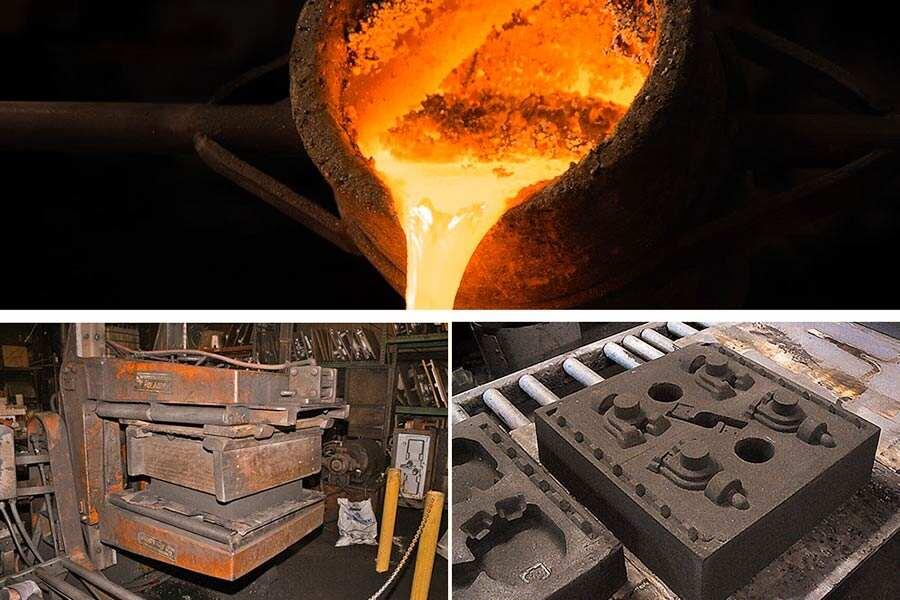
The sorcery of casting begins with a grain of sand, but this is not ordinary sand.Selecting the rightfoundry sandis the first key step in the success of a sand-cast component.
If asked, "Can I cast using beach sand?", the answer is straightforward:No.Natural sand composition, shape, and refractory properties (must withstand >1000°C) cannot be controlled, and quality andaccuracy of castingscannot be guaranteed.
Foundry sands arehighly engineered materials carefully selected or specially designed. From basic silica sands to high-performance zircon sands and chromite sands, from clay-bonded sands to chemically cured resin sands, there are so many varieties, each having unique characteristics and function.
This paper is intended to be your ultimate guide to choosing foundry sands.We will deconstruct the essential characteristics of typical foundry sands - composition, behavior, situations of applicability and key considerations. Guide you past general questions, learn to comprehensively appreciate the first pillar of casting success, andmake intelligent and informed sand selection choices for your project.
Comparison Table Of Essential Characteristics Of Foundry Sand Mold Systems
| Sand mold system | Core components | Advantages | Disadvantages | Most suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Sand | Silica sand + bentonite + water + additives (such as coal powder, starch) | Very low cost, reusable, high production efficiency, simple sand mixing and molding operations | Low dimensional accuracy, general surface finish, easy to produce moisture-related defects (pores, sand inclusions, sand holes), relatively low strength | Large-volume, relatively simple structure ferrous metal castings (such as gray cast iron, ductile iron castings, automotive parts, agricultural machinery parts, foundation pipes) |
| Resin-Bonded Sand | Silica sand + resin binder (furan, phenolic, alkaline phenolic, etc.) + curing agent (acid, ester, heat, gas) | Very high dimensional accuracy, good surface finish, high strength, suitable for manufacturing complex cores and castings, good disintegration | High cost, cannot be directly reused (regeneration treatment is required), odor and irritating gas (especially furan resin), curing time needs to be controlled | High-precision, complex inner cavity/structure castings (such as pump bodies, valves, gearboxes, machine tool parts, complex engine cores) |
| Coated Sand / Shell Sand | Silica sand + phenolic resin film (pre-wrapped on the surface of sand particles) | Excellent fluidity, fast curing speed (hot core box), high dimensional stability, excellent surface quality, very suitable for automated production, high sand core strength | High cost (raw materials and core making equipment), only suitable for hot core box or warm core box process, complex regeneration of old sand, high resin addition | Large-volume, complex thin-walled, high-precision casting cores (such as automobile engine cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, crankcases, hydraulic valve blocks) |
| Sodium Silicate Sand | Silica sand + water glass (Na₂SiO₃) | Low cost (especially materials), non-toxic and odorless, fast hardening (CO₂ blowing or self-hardening), relatively environmentally friendly, high strength | Poor collapsibility (difficult to clean old sand), strong hygroscopicity (resulting in reduced sand mold/core strength), difficult to recycle old sand, easy to produce "white frost" (Na₂CO₃) | Steel castings with medium and low precision requirements and large/thick-walled iron castings, single-piece small-batch production, and occasions with high environmental protection requirements |
Here’s What You’ll Learn:
- Three scientific pillars of sand casting:In-depth analysis of how base sand, binders, and additives work together to lay the foundation for successful casting.
- Wet Sand vs. Resin Sand:The Core Showdown: Revealing the 4 key performance comparisons of the industry leader (wet sand) and the precision expert (resin sand) in terms of cost, accuracy, and application.
- 60-second Sand Casting Decision Rule:Quick rule-of-thumb guide to metal type, component complexity, and cost budget to allow you to commit to the optimum sand mold system.
- Why is "regular" sand a "disaster recipe" for casting?From particle shape, purity through safety dangers, completely explain the 4 critical defects of play sand/beach sand.
- The Aluminum andSteel Sand CastingCode:Fully comprehend the crucial differences in the refractoriness and performance requirements of metals with different melting points (low requirements for aluminum versus extreme challenges for steel).
- The power of the core: building complexity inside out:Master the critical function of the internals and their optimization for cost and accuracy with the "composite application" method (green sand outer mold + resin sand core).
- Practical analysis:Sand casting championship solution for turbocharger housing: Let's take the case to see how seasoned foundries creatively incorporate sand mold technology to address the three issues of complex inner cavity, high precision and cost.
- Sand casting FAQs:answers that even old-timers may confuse: Solutions to key questions such as reusability of sand, channels for purchase, Petrobond sand characteristics, protection of sand processing from safety hazards, etc.
Now, let's brush away the dust and dive into the roots ofmetal casting- the art and science of sand casting, and find the perfect "sand key" for your project.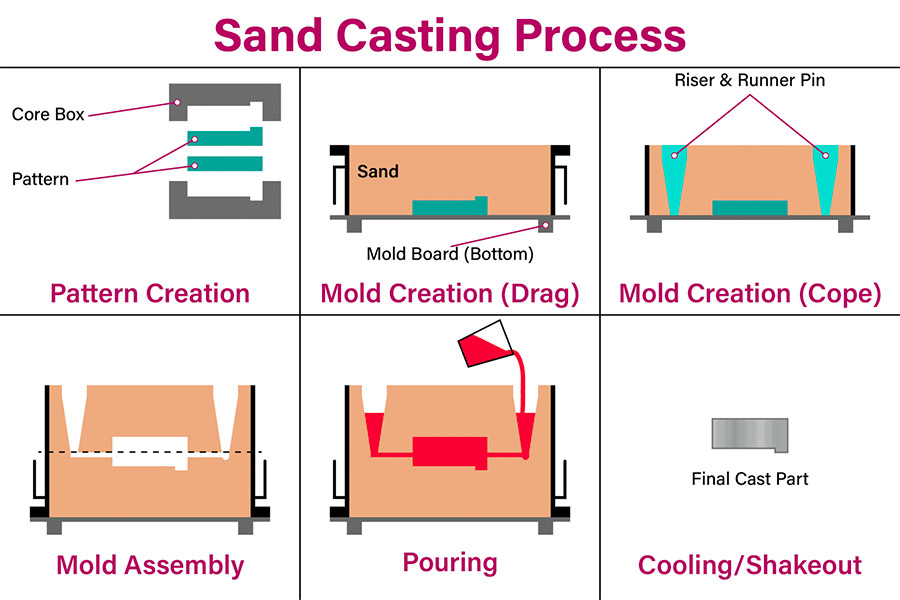
What Is "Casting Sand" Really? The Three Core Components
Casting sandis a core material used to create castings (sand molds) and cores in casting production. It is not a single component of sand but a complex system that is made up of different materials mixed in a fixed proportion. Its performance directly affects the strength, air permeability, refractoriness, and disintegration of the casting, which have direct impacts on the quality of the casting (dimensional accuracy, surface finish, internal defects, etc.) and efficiency of production as well. The casting sand system primarily comprises the following three basic components:
1. Base Sand
Base sand is the skeleton material of the casting mold, taking about 85%-95%.
Silica sand (popular choice):
Derived from natural quartzite, SiO₂ content ≥90%. Resistant to high temperatures (melting point 1713℃), low cost and readily available. It is, however, susceptible to reaction with metal oxides at high temperature to generate sand sticking defects, and needs to be used with additives.
Special sand (special conditions):
- Zircon sand:high content of ZrSiO₄, refractoriness above 2000℃, low thermal expansion rate, used for stainless steel/high temperature alloy precision casting, but the cost is 5-10 times that of silica sand.
- Chromite sand:mainly FeCr₂O₄, high heat conductivity, can prevent thermal cracking of heavy-walled castings, mainly used for largesteel castings.
- Olivine sand:Mg₂SiO₄-Fe₂SiO₄, no free SiO₂ dust hazard, suitable for high manganese steel casting.
2. Binder
Binder keeps the loose base sand in position, contributing 3%-10% to the mix.
Clay (traditional process):
Bentonite (montmorillonite mineral) forms a film of colloids when mixed with water to encapsulate the sand particles. The one used in wet sand process is 4%-8%, low in cost but in strength, and is suitable for small to medium castings.
Resins (precision casting):
- Furan resin:furfuryl alcohol formaldehyde resin, hardening at room temperature after acid catalyst addition, high strength, good disintegration, used widely on auto fittings.
- Phenolic resin:divided into hot core box (200℃ hardening) and cold core box (amine gas hardening), high efficiency of production, high precision of dimensions up to CT7 level.
Inorganic binder:
Water glass (Na₂O·mSiO₂) is self-hardened by absorbing CO₂ or adding ferrosilicon powder, no smoke pollution, but difficult to recycle old sand, primarily applied in large steel castings.
3. Additives
Additives absorb <5%, purpose-oriented performance optimization:
Coal powder (anti-sticking sand):
Addition ratio 2%-5%, thermal decomposition while pouring to form a reducing gas film, isolate the molten iron and sand mold, and smooth the cast iron surface (Ra≤12.5μm).
Sawdust/husk (to enhance air permeability):
Add 1%-3%, following high-temperature carbonization, microporous channels remain to vent cavity gas and prevent pore defects in castings, especially suitable for thick and large wet sand molds.
Other functional additives:
- Iron oxide powder:reduce vein defects in steel castings.
- Starch:improve wet strength (use in combination with bentonite).
- Boric acid:reduce high-temperature deformation (stainless steel casting).
The sand casting system is based on silica sand as matrix material, builds up mold strength with adhesives and uses additives to ensure process performance optimization. The three elements complement each other and strike a balance between cost, accuracy and requirements ofcasting quality.
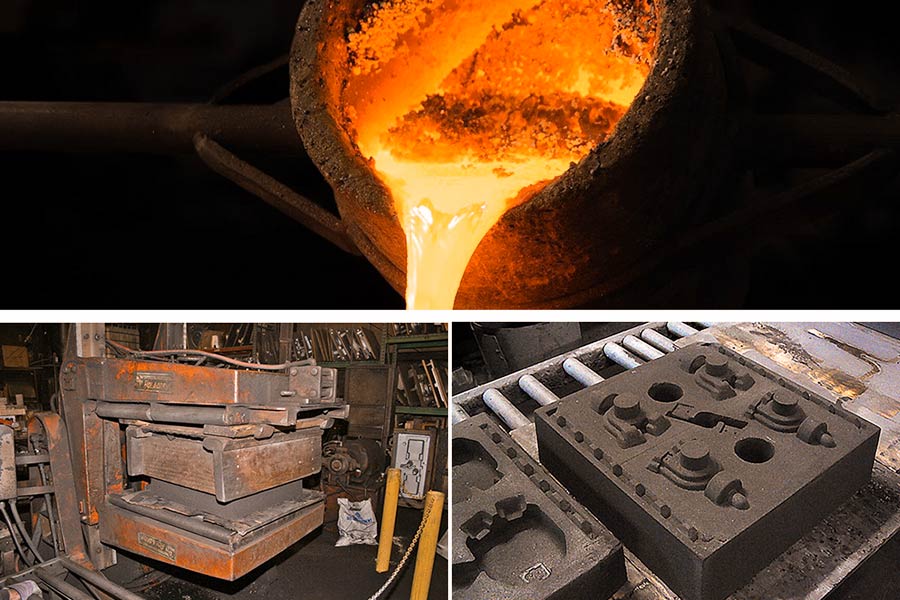

Deep Dive: Green Sand - The Industry's Workhorse
Green sand castingis the oldest, most widely used and cheapest method in sand casting, especially in mass production of small and medium castings with comparatively simple structures (e.g., auto parts, pipe fittings, agricultural equipment parts, simple mechanical parts). It is also the default option provided by the majority of online sand casting service providers, mainly due to its economy and convenience.
1. The nature of "Green" (wet)
"Green sand" is not a hue, but a water plastic state (3%-5% water content). Water combines with the binder (bentonite) to activate it, whereupon the sand grains form a pressure-sensitive flexible network that can be molded into cavities of any shape and will be structurally stable when demolded.
2. Working principle - bentonite and water co-star
The basic bonding system of green sand is bentonite + water + silica sand.
- Bentonite:A water-absorbing natural clay mineral (mainly montmorillonite). It is the basic binder of green sand.
- Water activation:Upon contact with water, the bentonite particles' layered structure absorbs water molecules and swells considerably (the volume may increase several times). This process is called hydration expansion.
- Bridge formation of the bonding:When water is absorbed and expanded, the bentonite particles become plastic and viscous. They will engulf the surface of the silica sand particle and form a viscous bentonite water film between the sand grains, like a "glue film."
- Mechanism of bond:The viscous water film holds the sand grains together by the following forces:
- Bond force:The viscosity of the bentonite water film itself.
- Capillary force:Water surface tension at the fine pore spaces between sand grains.
- Van der Waals force:Molecular attraction.
- Sand mold strength during forming:As the pounding takes place, pressure from the outside forces the sand grains together into close contact, and the bentonite water film forms progressively stronger "bonding bridges" at the points of contact of the sand grains. While withdrawing the external force, the bonding strength provided by these bonding bridges is sufficient green strength (Green Strength) to enable the sand mold to hold its shape, facilitate the process of handling and closing of the mold, and resist static pressure of molten metal in the pouring initial stage.
- Silica Sand:The major refractory aggregate (frequently 85%-95%), it provides the erosion and heat resistance of high-temperature molten metal. The particle size range determines the permeability andsurface finish.
3. Cost and efficiency benefits analysis
| Advantage dimensions | Specific performance |
|---|---|
| Material cost | Silica sand (≈$30/ton) + bentonite (≈$200/ton), the cost is only 1/5-1/3 of resin sand |
| Process efficiency | Sand can be used immediately after mixing, molding speed>120 molds/hour (machine molding), no need to wait for curing |
| Recyclability | Old sand is crushed and screened + water and soil filling, 95% can be reused, waste sand rate <5% |
| Equipment investment |
No baking/chemical hardening equipment is required, and the molding line cost is reduced by more than 40% |
► Why online casting services are desired:
It meets more than 80% of the requirements for small and medium-sized gray iron/ductile iron parts, the cost for each part is under control, and it can be accommodated to switch between quick proofing and batch orders.
4. Limitations: Why it does not work in all high-precision industries
(1)Dimensional faults due to humidity:
Shrinkage during drying (linear shrinkage rate 0.5%-1.2%), water vapor interface boiling in pouring, andsurface roughnessof the casting Ra>25μm (resin sand to Ra 6.3μm).
(2) Structural strength bottleneck:
Wet compressive strength <150kPa, unable to support complex core groups (e.g., engine cylinder water channel core), thin-walled structures (<3mm) are prone to deformation.
(3)Poor disintegration
At high temperature, bentonite sintered into a ceramic hard shell, which was not easy to wash out sand and easily destroyed the fine details of precision castings.
Common failure case: During green sand casting of automobile turbine housing (with cooling channel of 0.8mm), the yield rate was less than 60%, but the resin sand process could reach 95%.
5. Summary of Application Positioning
Green sand is currently the undisputed leading process for iron castings (specifically <50kg) with its incredible cost savings and efficient circulation capability. For areas of high precision (CT>8), detailed structure (>5 core group), and specialty alloys, however, it has to give way to precision processes such asresin sand/coated sand. Its technical character is an industrial paradigm with precise positioning in the triangle of cost, effectiveness, and performance.
Deep Dive: Resin-Bonded Sand - The Precision Specialist
| Features | Furan resin sand | Phenolic resin sand |
|---|---|---|
| Main resin types | Furan resin (furfuryl alcohol polymer) | Alkaline phenolic resin |
| Curing method | Acid curing (such as phosphoric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid) | Ester curing (such as organic ester) |
| Core advantages | High strength, fast hardening, good disintegration, low cost | Excellent high temperature strength, low gas emission, good resistance to sand sticking |
| Typical applicable parts | General precision castings such as hydraulic valve bodies, pump bodies, impellers, and housings | Large or thick-walled castings, alloy castings that are easy to stick to sand, and castings that require high dimensional accuracy at high temperatures |
1. Classification introduction
There are two main types of resin sand:
- Furan resin sand:Furan resin binder and acid curing agent (e.g., phosphoric acid) are employed. It has rapid hardening, high strength at room temperature, good disintegration, low cost, and extensive use.
- Phenolic resin sand:Mainly consists of alkaline phenolic resin sand, with organic ester as curing agent. It has nice high temperature strength, and low gas emission. It is suitable for casting large, thick-walled castings or easy-to-stick sand alloys, and has nice metal penetration resistance.
2. Working principle
Resin sand hardening is realized by chemical reaction:
- Mixing:Mix the raw sand (silica sand or special sand), resin binder and curing agent in proportion.
- Molding/core making:Fill the mixed sand into the mold or core box to shape and compact it.
- Hardening:Cross-linking and polymerization of the resin and curing agent occur at room temperature or a certain temperature, and a three-dimensional network of bonded sand particles is generated.
- Molding:Sand mold or sand core, after curing, has sufficient strength and can be ejected to retain an accurate shape.
- Pouring:Molten metal is poured into the cured resin sand mold cavity.
- Collapse:High-temperature metalcauses the resin bonding bridge to burn and deteriorate, and the sand mold/sand core collapses, with simple cleaning.
3. Advantages in detail: First choice for precision casting
In the manufacture of parts such as hydraulic valve bodies with high internal cavity finish, dimensional accuracy and geometric complexity, resin sand is the first choice:
- High dimensional accuracy and contour clearness:high strength, high rigidity, small deformation after curing, can replicate mold details, and ensure casting dimensional stability.
- Good surface finish:fine and even resin sand particles, the cavity surface is dense and smooth, which reduces the surface roughness of the casting and lowers machining.
- Strong ability to form very complex structures:high strength and fluidity, can form complex, thin-walled, hollow inner cavity structures.
- Good collapse:The resin collapses after pouring, and the sand mold/sand core falls off by itself, with simple cleaning of the complex inner cavity.
- Good production efficiency and stability:rapid hardening, fast demolding and cycle production; precise process controlling, stable casting quality.
4. Cost-influencing factors: key considerations for custom sand casting
Resin sand affects the cost of custom sand casting:
- High material cost:Resin and curing agent are more costly than traditional clay sand binder.
- High process control requirements:Sand mixing ratio, temperature and humidity, curing time, etc. need to be precisely controlled, and the equipment and management requirements are high.
Core value:In spite of the high initial material price, high precision, high surface quality, complex parts molding ability and post-processing cost savings can be obtained. It is more competitive in precision and complex parts production cost overall. The reason for selecting it is to obtain more added value.
Resin sand has become the backbone of custom sand casting forprecision castingsin large industries such as hydraulics, pumps and valves with its chemical hardening precision capabilities and high-quality casting, and is a significant factor affecting the overall cost-effectiveness.
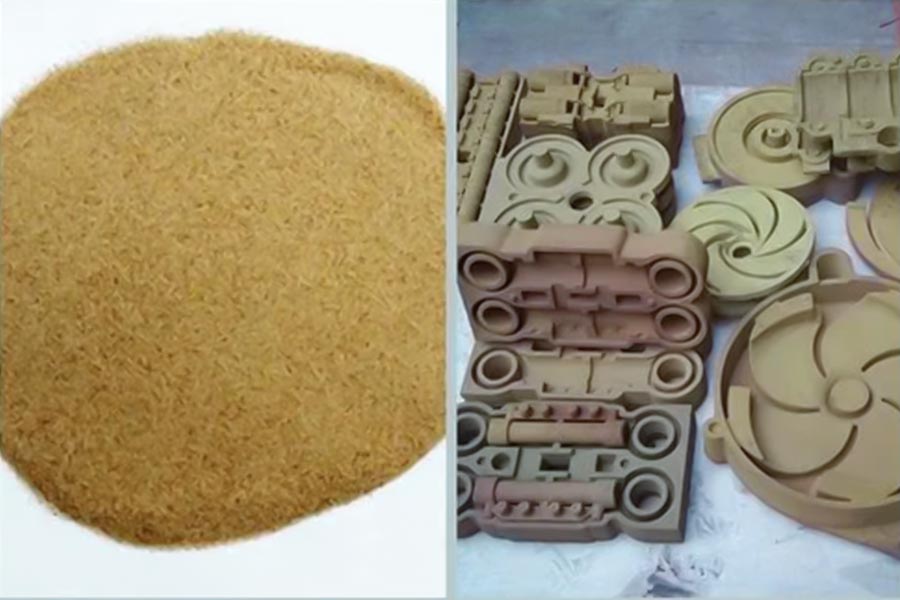

The Critical Question: Why Can't I Use Play Sand or Beach Sand?
The main reasons why play sand (i.e., sand for children's sand pits) and beach sand are not suitable as a replacement for foundry sand for metal casting are:
1. Differences in particle shape lead to unstable structure:
The single most significant property of foundry sand is its non-angular particle shape. This irregular particle shape enables the sand grains to "bite" securely and lock tightly, forming a mold cavity of the required strength and stability. On the other hand, play sand or beach sand grains are highly rounded due to long-term wind and wave abrasion. The smooth surface greatly reduces the friction and mechanical interlocking ability between grains, causing the sand mold structure to be loose and easy to collapse and not able to resist gravity and erosion of the molten metal, and easy to collapse.
2. High impurity content causes casting defects:
Natural sand (especially beach sand) contains a large amount of harmful impurities, such as organic matter, shell fragments, salt (chloride) and various minerals. When high-temperature molten metal (usually over 1000°C) is poured, these impurities will burn, decompose or gasify violently, producing a large amount of gas (H₂O steam, CO₂, Cl₂, etc.). If the gas cannot be discharged from the mold in time, serious defects such as pores, pinholes or surface pits will form inside or on the surface of the casting, significantly reducing the quality and strength of the casting.
3. Lack of necessary binders and inability to form:
Foundry sand (especially natural silica sand) usually contains a certain proportion of natural clay (such as bentonite), or such binders need to be added artificially. Clay produces viscosity and plasticity when it comes into contact with water. It is the core of forming bonding between sand particles and making the sand mold obtain sufficient wet strength and plasticity. Play sand or beach sand is washed or formed naturally, and the effective clay content is extremely low or zero. Even if water is added, it cannot be effectively shaped due to the lack of bonding medium, and a mold with sufficient holding power cannot be made.
4. Safety hazards cannot be ignored:
There are significant safety risks in using untreated natural sand. The residual water in the sand (especially crystal water or capillary water) vaporizes instantly when it comes into contact with high-temperature molten metal, and the volume expands rapidly, which may cause steam explosion inside the mold, splashing molten metal and hot sand, endangering the operator. In addition, natural sand often has a higher dust content and a complex composition (it may contain silica dust, salt dust, unknown mineral dust, etc.). Long-term inhalation poses a serious threat to the respiratory health of workers, far exceeding the processed sand that meets foundry standards.
How Metal Type Dictates Sand Choice: Aluminum vs. Steel
Comparison of the influence of metal type on sand mold selection
| Characteristics | Casting Aluminum | Casting Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | Low (~660°C) | Very high (>1370°C) |
| Sand mold requirements | Low refractoriness requirements | Strict refractoriness and thermal shock resistance requirements |
| Common sand molds | High-quality green sand | High-performance resin sand |
| Advantages | Economical and easy to shape | Good high temperature stability and strong resistance to metal penetration |
| Special considerations | Petrobond sand (oil-based) is used for fine details | Special sands (such as chromite sand) are often required for key parts |
1. Cast aluminum:
- Low melting point advantage:The low melting point of aluminum (~660°C) means that the sand mold is subjected to a lower thermal load during pouring.
- Sand mold selection:The refractoriness requirements for sand molds are relatively loose. High-quality green sand (with bentonite as a binder and appropriate amount of water) is the most widely used sand mold for aluminum casting due to its good plasticity, strength and cost-effectiveness. It is strong enough to withstand the thermal shock of molten aluminum without severe sintering or deformation.
- Fine applications:For small castings or hobbyist applications that need to capture very fine details, Petrobond sand (an oil-based bonded sand) is popular. It can provide excellent surface finish and detail reproduction, and the sand is easy to fall off.
2. Cast steel:
- High temperature challenge:The extremely high melting point (>1370°C) and greater heat capacity of steel pose a severe test to sand molds.
- Strict requirements:Sand molds must have extremely high refractoriness to prevent the sand grains themselves from melting and sintering on the surface of the casting (sand sticking). At the same time, excellent thermal shock resistance is required to resist the huge thermal stress generated when molten steel is injected to avoid sand mold cracking or sand washing. Good high temperature strength and resistance to metal penetration are also required.
- Sand mold selection:High-performance resin sand (such as furan resin sand, phenolic resin sand) is the mainstream choice. They provide high temperature strength and dimensional stability far higher than green sand through chemical bonding, and can better withstand the high temperature impact of molten steel.
Key parts protection:For thick and large sections of castings, hot joints or parts requiring extremely high surface quality, more expensive special sands such as chromite sand are usually used locally. Chromite sand has extremely high refractoriness, excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to metal penetration, which can effectively prevent sand sticking and penetration defects, but the cost is very high.
The melting point of the metal directly determines the temperature limit that the sand mold needs to withstand, and then determines the core performance requirements of the sand mold such as refractoriness and strength.Cast aluminumcan use economical green sand due to its low temperature, while the high temperature of cast steel requires the use of high-performance resin sand or even special sand.
Case Brief: High-precision Casting Solution for Turbocharger Housing
Challenges:
When developing a turbocharger housing for a customer, we encountered a core difficulty: its internal structure contains extremely complex and precise spiral channels, which require extremely high dimensional accuracy. At the same time, the casting must maintain reliable performance in the high temperature and high pressure environment where the turbocharger actually works. This puts a severe test on thecasting process- it must be able to perfectly replicate the complex internal cavity while ensuringsurface qualityand dimensional stability.
Common Misunderstandings and Limitations:
We found that if we rely entirely on the traditional green sand process to produce this part, there are fundamental deficiencies: the complex spiral channels are difficult to accurately shape, and the surface of the casting obtained by green sand is relatively rough. This roughness will seriously interfere with the internal airflow (aerodynamic efficiency), directly affecting the performance and efficiency of the turbocharger, and cannot meet the requirements of stringent working conditions.
LS's professional solution:
To overcome this problem, we innovatively adopted the combined sand casting technology:
- Core key - internal spiral channel:For the most complex and demanding internal spiral channel, we specially selected high-strength resin sand to make precision cores. This material has excellent high-temperature strength and dimensional stability, which can ensure the smooth and precise molding of complex channels to meet the needs of aerodynamics and high temperature and high pressure resistance.
- Cost optimization - external main structure:For the main part of the housing, we fully utilized the good cost-effectiveness and molding ability of green sand to make external molds.
Results and value:
Through this differentiated and combined application ofsand technologystrategy, we successfully:
- Guaranteed core performance:The internal key channel achieved the required high precision, high finish and high temperature and high pressure resistance.
- Effectively controlled costs:Maximized the economy of the process while ensuring the most critical performance.
- Achieved reliable delivery:Provided customers with turbocharger housing castings that meet stringent working conditions and have excellent performance.
This case fully demonstrates the professional ability of theLS casting teamto deeply understand product requirements, accurately select and optimize processes.We are good at providing customers with the most cost-competitive casting solutions while meeting extreme technical requirements through innovative process combinations.

FAQs
1. Can foundry sand be reused?
Yes, but it depends on the type of sand. Green sand can be reused directly by simply drying and remixing due to its water-based binder properties, which is low-cost and easy to operate. Resin sand is different. It uses chemical binders and must go through an expensive regeneration process (such as thermal regeneration or mechanical regeneration) to remove the old resin and recover the sand particles. This process requires professional equipment and is costly, so frequent reuse is not recommended.
2. Where can I buy foundry sand?
Foundry sand usually needs to be purchased from professional industrial material suppliers, such as wholesalers or manufacturers specializing in foundry, metallurgical or engineering materials, rather than ordinary hardware stores or retail stores. It is recommended to check the supplier directory through industry exhibitions, online B2B platforms (such as Alibaba Industrial Products) or local yellow pages to ensure that the quality of the sand meets the casting standards (such as particle size, purity), and pay attention to whether the supplier provides technical support and logistics services to avoid purchasing unsuitable or low-quality products.
3. What is the difference between Petrobond sand and green sand?
The main difference lies in the type of binder and performance: Petrobond sand uses oil-based binders (such as petroleum derivatives), which can provide finer casting details and higher strength, and is suitable for complex molds, but the disadvantage is that it produces more smoke and odor duringhigh-temperature casting, and ventilation needs to be strengthened; green sand uses water-based binders (such as bentonite), which is lower in cost, easy to handle and environmentally friendly, but the details are slightly worse, and it is more suitable for simple casting projects. When choosing, you need to weigh the detail accuracy and operating environment according to the project requirements.
4. Is the sand treatment process safe?
Yes, thesand treatment processis generally safe in a professional factory environment, but safety regulations must be strictly followed: including the installation of efficient ventilation and dust removal systems to reduce the spread of silica dust, and operators must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) throughout the process, such as N95 masks, goggles and gloves to prevent inhalation of harmful dust (such as silica dust may cause silicosis). In addition, factories should conduct regular equipment maintenance and air quality testing to ensure that the treatment process (such as sand mixing or regeneration) is free of leakage or explosion risks. It is not recommended for individual home workshops to try this.
Summary
Choosing foundry sand is no small matter. It is a rigorous science that directly determines the final quality of the casting, production costs and overall efficiency. To reiterate the core point: ordinary sand (such as construction sand, river sand) is not suitable forprofessional castingproduction because of its insufficient refractoriness, poor air permeability, low strength and unstable composition. It is very easy to burst, sinter or produce pores when exposed to high-temperature molten metal, resulting in the scrapping of castings.
Choosing the right sand mold system for your project can be complicated. Instead of getting lost in the sea of sand, it is better to leave this critical decision to the experts!Upload your designfiles to our secure online platform now. Our engineers will not only provide you with a transparentsand casting quotation, but also conduct in-depth analysis and accurately select the most suitable sand mold system for you to ensure that your project is on the right track from the first step!
📞Tel: +86 185 6675 9667
📧Email: info@longshengmfg.com
🌐Website:https://lsrpf.com/
Disclaimer
The contents of this page are for informational purposes only.LS seriesThere are no representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that a third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design characteristics, material quality and type or workmanship through the LS network. It's the buyer's responsibilityRequire parts quotationIdentify specific requirements for these sections.Please contact us for more information.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal manufacturing,3D printing,Injection molding,Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseLS technologyThis means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:www.lsrpf.com