Have you ever cut a piece of acrylic with great expectations, only to find that the edges aren't smooth, but instead rough, sticky, or even feature ugly burn marks, instead of the glass-like smoothness and sharpness that you had hoped for? Or when you carefully engrave, you end up with a blurry or even melted "disaster" instead of a clear and subtle frosted effect?
Don't be so fast to blame your laser machine! Ninety percent of the time, the problem is not with the machine, but with the deceptively simple acrylic sheet in your hand.If you have the wrong acrylic, all your design effort can instantly go from "potential boutique" to "trash."Low-quality or the wrong acrylic for laser processing will not only greatly reduce the effect, but may even release toxic gases and even damage the machine.
Which acrylic is the "true son" oflaser cuttingandengraving? The answer lies in the molecular structure of the sheet.
Cast Acrylic vs. Extruded Acrylic: The Basic Differences in Laser Cutting
| Features | Cast Acrylic | Extruded Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Edge Quality | Ice-smooth, burr-free | Polished well, but may have slight burrs |
| Engraving Effect | Vivid matte/frost white with high contrast | Engraved remains relatively transparent, with low contrast |
| Thickness Tolerance | ±10% (less uniform) | ±10% (less uniform) |
| Price | Higher | More economical |
This guide will take a step-by-step walkthrough of the essential distinctions between these twoacrylics for laser cutting, from manufacturing process to everyday use, and through a practical example, show how this choice has a direct impact on the expense and final result of your project.
Here's What You'll Learn:
- The essential difference in manufacturing process:In-depth exploration of the main distinctions betweencast and extruded acrylicfrom liquid to molded state, and how it affects material qualities.
- The key difference between cutting and engraving effects:Discover which acrylic is the "king of cutting" and which is the "king of engraving", and the deciding difference in their cut edges and engraved surfaces.
- The deadly impact of thickness tolerance on precision design:Discover the huge difference in thickness consistency between cast and extruded acrylic, and why it's crucial for your structural parts.
- High-end case from real project:Learn how a cosmetics display stand in a high-end mall transformed from "cheap and blurry" to "elegant and clear" through the correct selection of acrylic.
- Mastering acrylic cutting professional parameter recommendations:Master the major principles of speed, power, and air assist settings for cast and extruded acrylic to avoid testing waste of expensive material.
Let's start learning more and becoming a trueacrylic materialselection master.
Why Trust Our Analysis? Our Lasers Cut Them Every Day
I’m Gloria, an engineer at LS.Our advice on the choice ofcast vs. extruded acrylicis not just talk, but comes fromreal experience working side by side with lasers every day.
At LS, ourlaser cutters process both materials day in and day out. I’ve seen it with my own eyes and hands:
- The form under the laser:cast acrylic is as transparent and smooth as flame polishing;extruded acrylicshows different states of melting and edge effects.
- Sensory confirmation:there is a subtle difference in the smell when they are being cut, and the morphology of the waste and the treatments used are also completely different. These are "first-hand information" that can be accumulated only by being there.
As a professionallaser cutting partsmanufacturer, the actual experience of thousands of projects is our foundation. We know the results of choosing the wrong material: burrs, whitening, low efficiency, and even affecting the final quality and cost of the product.
Our suggestion has only one aim: to rescue you from these traps. Your choice of the right acrylic and coordination with our efficient procedure are the sole means to the ultimate finished product at the most cost-effective laser cutting price.
Trust LS's expertisein "cutting" with lasers, and let us help you bring your design to life with precision.
Why So Much Great Range of Difference Between Cast And Extruded Acrylic?
"To observe how they work, you need to observe how they are made."
Acrylic (polymethyl methacrylate, PMMA) of the same transparent sheet appearance has different "personalities" and "abilities" due to different birth processes (casting or extrusion). The reason for the difference essentially lies in their method of production. Let us start with the main differences in a simple table:
Cast Acrylic vs Extruded Acrylic Core Difference Comparison
| Features | Cast Acrylic | Extruded Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing process | Liquid monomer (MMA) is poured into the glass mold and solidified. | Solid particles are heated and melted, and forced through the mold to be extruded |
| Process metaphor | "baking a cake in a mold" | "squeezing toothpaste in a toothpaste tube" |
| Molecular structure | Higher molecular weight, random molecular chains | Relatively low molecular weight, molecular chains are oriented along the extrusion direction |
| Internal stress | Very small stress | Large stress (especially along the extrusion direction) |
| Core characteristics | Higher hardness, better chemical resistance | Softer, lower melting point |
| Thickness accuracy | Relatively uneven thickness | Extremely uniform thickness |
1. Cast acrylic: Formed "castings" through gradual shaping
(1) Process:Liquid MMA monomer is filled into the glass mold and slowly heated and cured (e.g., water bath).
(2) Outcomes:
High molecular weight:Gradual curing extends the molecular chain.
Random molecular chains:Uncontrolled curing of liquids to form a random network.
Very low internal stress:Mild cure and even shrinkage.
(3) Properties:
- Good hardness and higher scratch resistance (high molecular weight + dense structure).
- Improved chemical resistance (stable form).
- Optical purity/weather resistance generally improved.
- Thickness slightly irregular (usually slightly thicker at edges).
2. Extruded acrylic: Smooth and unbroken "extruded strips"
(1) Process:Acrylic particlesare melted and warmed, forced out through a flat mold under high pressure, calendered by a calender roller, and cooled to produce (uninterrupted production).
(2) Results:
Molecular chain orientation:High pressure extrusion and drawing orients chains in the machine direction.
High internal stress:Traps directional stress by quenching.
Low molecular weight:High temperature shear slightly degrades the molecular chain.
(3) Properties:
- Softer, lower melting point/heat deformation temperature (readily heat moldable).
- Extremely uniform thickness (precision mold and calendering).
- High batch consistency.
- Susceptible to stress cracking (treat with care in processing or solvent exposure).
- Slightly poor chemical resistance (especially to alcohols and ketones).
The "random network" of casting improves strength and purity, and the "directional arrangement" of extrusion improves uniformity and efficiency. The two fundamentally dissimilar "molecular life trajectories" converge to establish the performance watershed of theacrylic world.
Laser Cutting Showdown: Who Is The King Of Cutting? Who Is The King Of Engraving?
"Now, let's place them in the laser cutting machine and see what happens." The showdown between thelaser beamand different acrylics will be interpreted in completely different wonderful chapters. The outcome of this contest has already been determined by the inherent genes of the materials.
| Features | Extruded Acrylic | Cast Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Effect | Best in Cutting: Flame polished edge, extremely bright and smooth. | Clean edge with frosted/satin texture. |
| Suitable for Cutting | Pure cutting applications, high gloss edge required. | Cutting applications, frosted edge acceptable. |
| Engraving Effect | Light traces, basically transparent, low contrast. | Best in Engraving: Vivid frosted white, high contrast. |
| Suitable for Engraving | Not suitable for engraving requiring clear patterns. | Ideal for fine engraving such as medals, signs, artwork, etc. |
Cutting:
- Extruded acrylic is the unbeaten "king of cutting". The lower melting point causes the edges to melt and resolidify when cut with a laser, creating a natural "flame polished" finish with extremely smooth, crystal clear edges. It is used most often for those applications requiring only cutting and calling for an absolutely brilliant edge (such as display racks and contour cut parts).
- Cast acrylic has a similarly defined edge when cut, but because of its molecular structure and higher melting point, it does not create a flame polish, but instead provides an even matte or satin effect. This type of effect is also utilized in certain designs.
Engraving:
Cast acrylic is the most "king of engraving" material in engraving. When one uses a laser on its surface, it will leave a dense, opaque frosted white mark of engraving, which possesses extremely high contrast with unengraved transparent background. Thus, it is the perfect material to create medals, nameplates, logos, and artwork of complicated patterns or characters, with distinct and crisp patterns and professional taste.
Extruded acrylic is not suitable underlaser engraving. Thelaser engravingmarks are extremely weak and barely affect the transparency, resulting in extremely low contrast between the engraving and background, and a fuzzy visual effect. If the design requires a visible engraving or text, do not use extruded acrylic.
In acrylic laser processing, extruded acrylic is the "cutting king" with flawless cut edges that areflame-polishedand cast acrylic is the "engraving king" with the frosted white high-contrast bright engraving effect.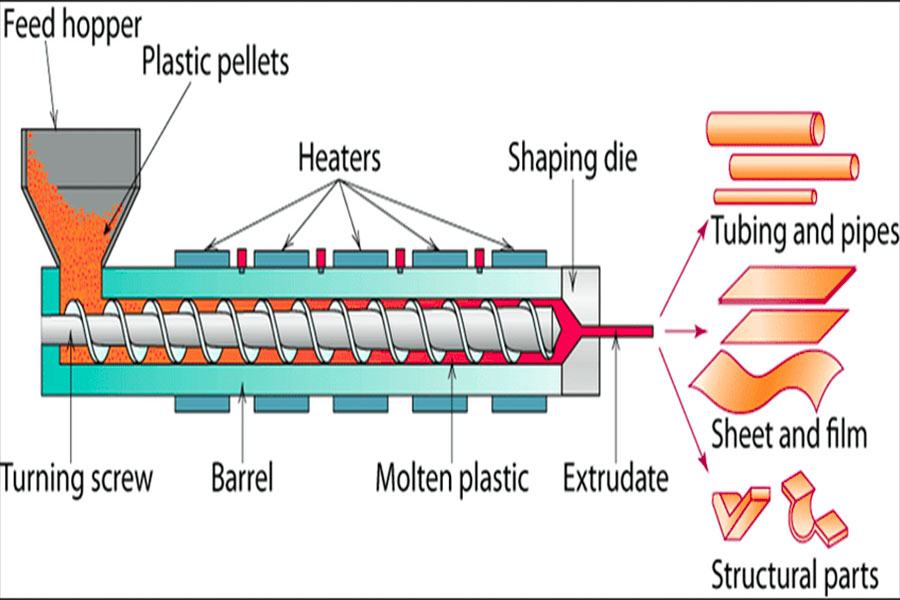
Thickness And Tolerance: Why It Matters To Your Design?
"A detail that is often neglected but can turn your precision design into a wreck."
In accuracy design, material selection is generally focused on strength, transparency or cost, but a seemingly trivial parameter - thickness tolerance - will generally be undervalued for its catastrophic potential. It is more or less an invisible line of defense in the design. Lost, it can lead to failure of assembly, malfunction, and even rework of the whole project. The table below briefly describes the main distinctions in thickness tolerance between extruded and cast acrylic:
| Characteristics | Extruded acrylic | Cast acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness tolerance | Very small (usually within ±5%) | Large (up to ±10%) |
| Material characteristics | Molecular chain has strong directionality and precise production process control | Molecular chain is randomly arranged, and curing shrinkage causes thickness fluctuations |
| Typical effects | Dimensionally stable, suitable for precision matching | Thickness has obvious fluctuations |
| Design suggestions | First choice for structural parts that require high-precision splicing and buckles | Be cautious, and the design must reserve a larger tolerance |
1. Advantages of extruded acrylic - Guarantee of precision:
(1) Theextrusion processitself (continuously extruding molten material through aprecision moldand forming it by cooling) enables it to offer very tight thickness control.
(2) A tolerance of ±5% would mean that, for example, a nominally 5mm extruded sheet will almost certainly have an actual thickness between 4.75mm and 5.25mm. This degree of consistency is the basis of precision design.
(3) Application scenarios: When your design necessitates precise splicing of multiple sheets (e.g., seamless display boxes), snap-fit features that require close fitting (e.g., instrument housings, drawers), or mechanical parts that require precise dimension location (e.g., guide rails, partitions), extruded acrylic provides a stable dimension foundation. Designers can design more confidently to nominal size, with fewer risks of assembly issues caused by variablematerial thickness.
2. Disadvantages of cast acrylic - Issues arising due to variations:
(1) Theprocess of casting(filling liquid monomer in the mold for curing and polymerization) will naturally result in gigantic variations in the thickness of different areas of the sheet due to mold deformation and curing shrinkage, etc.
(2) ±10% tolerance is a real hazard. A nominally 3mm cast sheet, for example, might be anywhere between 2.7mm and 3.3mm at various locations. Such inconsistency is catastrophic for designs that rely on precise dimensional fit.
(3) Design trap: If a component has a slot being designed and a slot width is designed to fit a 3mm sheet (without thinking about tolerance), then:
When a section with 3.3mm thickness is found, pushing the sheet in is impossible or forceful pushing will cause over-stress of the material and cracking.
When a section of 2.7mm thickness is found, the sheet will obviously become loose in the slot and lose the fixing effect, which will affect the structural strength and appearance.
3. Countermeasures:
- Have a wider design tolerance:You cannot apply the nominal thickness (e.g., 3mm) itself to designing slots, slots, and clearances fit. You need to consider the maximum thickness possible (e.g., 3.3mm) and the minimum thickness possible (e.g., 2.7mm).
- Make the gap larger:The width of the slot should be wider than the greatest expected thickness (for instance, 3.3mm + 0.1-0.2mm assembly gap) so that the thickest piece can fit in comfortably.
- Consider elasticity or filling:To avoid looseness in components, one may need to include elastic elements (such as silicone pads) or add fillers (such as glue) post-assembly to compensate for the gap in slender areas. That, however, increases complexity and expense.
- Use with caution in critical areas:Where very stringent fitting precision is required in critical structures, use casting plates of high tolerance only if verification and compensation measures are sufficient.
In precision engineering, the nominal thickness of the material is just the starting point. Tightly controlledthickness toleranceis the invisible line of defense to realize your design intention and avoid assembly disasters.

Case Study: Material Selection Process For A Luxury Cosmetics Display Stand
1. Project Background: We designed a bespoke luxury countertop display stand for an upscale cosmetics firm. The key highlight was to infuse crystal clear texture along with clear and elegant brand logo engraving effects.
2. Initial Plan and Issues:
Material Selection:In consideration of the initial cost criterion, we used extruded acrylic to develop the first prototype.
Prototype Feedback
Advantages:The cutting edge following CNC machining can meet the demands of brightness and smoothness.
Key Issues:The laser engraving effect of the logo was below expectations far. The engraved part was indistinct and rough, which appeared cheaply visually and greatly harmed the high-end positioning of the brand.
3. Engineering Analysis and Solution Optimization:
- Problem Diagnosis:The internal stress and molecular orientation resulting from extruded acrylic due to its production process made it difficult to achieve a subtle and even surface etching effect when laser engraving.
- Optimization Solution:We immediately conceptualized and created a second prototype from cast acrylic.
Comparison and strengths of solutions:
- Cutting process: Cast acrylic is also able to achieve high-smooth precision cutting edges.
- Engraving process:Laser engraving, with its more uniform molecular composition and better optical characteristics, has the ability to produce a sharp-edge, precise clear, sophisticated matte finish effect that significantly raises the visual grade.
- Cost effect:The cost of processing an individual item with laser engraving has thus increased by around 20%.
4. Final effects and value:
Compared to the two physical models, the customer was easily able to identify the overwhelming advantage of cast acrylic in highlighting the luxurious feel and crystal clearness of the brand logo. Although the piece is more expensive, thefinished productis precisely what the luxury image positioning of the brand calls for, adequately captures the brand value among the market, and has been met with positive reception by the customers.
LS engineer summary:Below is an example strongly supporting material science's function in driving expressiveness in end goods. In the high-end display market pursuing the ultimate look and feel, the choice of material with specific optical and process attributes (in this case, cast acrylic) overrides control of the material's initial cost. With professional content expertise,prototypescreening and open cost-benefit analysis, we would be able to guide our clients to the appropriate choice and guarantee flawless fulfillment of the objectives of the project.
Specialty Acrylics: Colored, Mirrored And Fluorescent Acrylics
| Type | Process characteristics | Core advantages | Typical applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colored acrylic | Mostly cast, easy to add pigments | Can produce strong color contrast when engraved | Signs, displays, decorative pieces |
| Mirror acrylic | Transparent extruded board with mirror film on the back | Mirror-like surface, strong modern feel | Mirror decoration, reflective signs, furniture |
| Fluorescent acrylic | Special casting process, edge light guide | Edge emits bright fluorescence under light | Backlit signs, luminous decorations, art installations |
- Colored acrylic: Made mainly by the casting process, the color is embedded in the material. The great advantage is that whenengraved or cut, the engraved area will produce a bright and beautiful contrast with the main color, which visually is highly effective.
- Mirror acrylic:It is a clear extruded acrylic sheet, and the mirror effect is achieved by having a high-quality mirror coating applied to the rear side. When processing (especially cutting), care should be taken to work from the back and modify machine parameters (such as power and speed) to prevent cracking or burning of the front mirror layer.
- Fluorescent acrylic (Edge-Lit):Made via a special casting procedure, its feature attribute is edge-guided light emission. When light is fed from its edge, the entire edge of the sheet will emit a bright and vivid light, which is extremely suitable for the production of extremely eye-catching glowing signage and ornaments at night or in dark locations.
Colored, mirrored and fluorescent acrylics have greatly expanded the application field ofacrylic materialby their particular optical effects and processing capabilities, vividly illustrating "the world of acrylic is much more than transparent", and introducing innovative potential to design that goes beyond conventional perception.
How To Set The Right Parameters For Your Laser Cutting Machine?
Choosing the material correctly is just the start, and parameter setting is the key tosuccessful cutting. Especially when cutting acrylic materials, the parameter settings for different types of acrylic vary significantly:
- Extruded acrylic:A relativelyhigh cutting speedand low power are recommended to achieve a smooth edge as in flame polishing. This will melt the surface of the material quickly to create a polishing effect, and prevent over-melting that will result in edge collapse or distortion.
- Cast acrylic:When you pursue a clean cut appearance and clear and detailed engraving lettering, you need relatively lowcutting speedand high power. Sufficient power can ensure full penetration of the material, and low speed can ensure that the cutting face is even and vertical, with less dross.
Never apply "general parameters"! Always test on a scrap piece of material beforecutting expensive materials. This is a required step:
System test: Test the power, speed, and frequency (PPI) combination.
- Observe and analyze:carefully examine the cut quality (smoothness, verticality, dross), engraving depth and clarity, and back-side effects.
Fine-tune and lock: fine-tune based on test results to reach the parameters that are perfectly matched to your specific machine, material batch, and desired result. - Strong air assist is a "right-hand man" to acrylic cutting. It can blow the melt away rapidly and has the effect of suppressing the flame generated during cutting, directly leading to cleaner, carbon-free, high-quality cuts, which is of great value in achieving professional effects.
The key to successful cutting is to intimately understand thematerial properties(e.g., distinguish between extruded acrylic and cast acrylic), establish the ideal power, speed and frequency combination via rigorous scrap testing, and always activate the robust air assist feature to convert parameters into optimum cutting results.

FAQ - Outstanding Questions About Acrylic Laser Cutting
1. Is laser cutting of acrylic toxic?
Acrylic (PMMA) is mostly degraded into non-toxic or low-toxic monomers while laser cutting, and there are no highly toxic substances produced. Nevertheless, there are intense irritating odors and smoke emitted while cutting, which may be disagreeable if inhaled for a long time. Therefore, a strong ventilation and smoke exhaust system must be equipped to ensure a safe working environment, protect the health of staff, and keep the equipment clean.
2. Why can't PVC and polycarbonate (PC) be cut with a laser?
PVC contains chlorine elements, which will emit highly toxic chlorine gas when laser-cut, harming the human body and being highly corrosive to the internal components of the laser equipment.Polycarbonate (PC)is highly susceptible to burning, melting, and producing carbonized black edges when burned by a high-temperature laser, and there can be no clean cutting effect achieved. Neither of these meets the safety standards oflaser processingand must be avoided.
3. What is the thickness of the acrylic?
The thickness option is aligned with practical use: 3mm is suitable for decorative items such as signs and light boxes; 5mm and above are suitable for load-supporting structural elements. It should be stressed that additional thickness will have a significant effect on processing efficiency - thicker boards require higher laser power and lower cutting speed - resulting in additional processing time and money. One is advised to consider overall based on load-bearing requirements and budget.
Summary
The choice of using cast or extrudedacrylic for laser cuttingis not a simple "right" and "wrong," but more of a "good" and "bad" decision. It directly affects the final result, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of your project.
Seeking excellent engraving details and edge transparency? Choose cast acrylic.Its uniform molecular structure and excellent thermal stability make it the first choice for fine engraving (especially deep engraving, three-dimensional engraving) and applications that require crystal-clear cut edges.
Put economy and splicing bond strength first? Choose extruded acrylic.Its economy and super seamless splicing achieved when solvent bonding make it a first choice for large area coverage, structure building or budget-limited projects.
Understanding the fundamental differences in cast and extruded acrylic performance in laser processing - from molecular structure to heat response to physical characteristics of the finished product - is the secret to making your project a success. Don't let bewildering material choice stand in the way of your innovative design.
Let LS's Team Of Experts Guide You!
Upload your design files to our secure site today. Not only will we provide you with a highly competitivelaser cutting quote, but our veteran engineers will also recommend exactly the type of acrylic material (cast or extruded) that most effectively provides the visual effect and performance requirements required by the critical aspects of your design (are you considering fine engraving or structural splicing? Is it more decorative or functional?). Experience a truly personalized service based on professional advice to protect your project!
So when you are thinking "Which acrylic to use for laser cutting?", simply remember: use casting for engraving and extrusion for splicing. Decide your needs and exactly pair them to produce perfect works.LS's professional guidanceis the missing piece to your success.
📞Tel: +86 185 6675 9667
📧Email: info@longshengmfg.com
🌐Website:https://lsrpf.com/
Disclaimer
The contents of this page are for informational purposes only.LS seriesThere are no representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that a third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design characteristics, material quality and type or workmanship through the LS network. It's the buyer's responsibilityRequire parts quotationIdentify specific requirements for these sections.Please contact us for more information.
LS Team
LS is an industry-leading companyFocus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precisionCNC machining,Sheet metal manufacturing,3D printing,Injection molding,Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. chooseLS technologyThis means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:www.lsrpf.com