Precision CNC turning services can be crucial to the engineers and procurement managers who require dependable quality in machined parts on a continuous basis. However, it is challenging on their part to strike a balance between dimensional tolerancing, material, and cost. Inequitable results and misunderstandings at the supply side can be costly in terms of time as well.
These kinds of problems are primarily caused due to the lack of knowledge about technology, lack of quality control, or ignorance of demands in high-intensive applications by the supplier. Outsourcing technically difficult components to such suppliers can pose tremendous risks. It will be analyzed in this paper how the systematic and collaboration-based approach of LS Manufacturing can be helpful in not only making precision CNC turning an outsourcing task but also helping such processes go beyond outsourcing.

Precision CNC Turning Services: Quick Reference Guide
| Section | Key Focus | Core Offerings / Solutions | Client Benefit |
| Introduction | Understanding Common Pain Points in Outsourcing: Quality, Cost, Speed. | Highlighting the gap between standard and precision services. | Identifies the need for a specialized, reliable partner. |
| The Challenge | Root causes: supplier capability, quality systems, understanding. | Analyzing risks of choosing inadequate suppliers | Frames the necessity for technical expertise and process control. |
| Our Solution | Systematic process addressing risks of outsourcing. | 1. Systematic Process; 2. Data; 3. Partnership Model | Engages Procurement to become Performance and Total Cost Leaders. |
| Technical Capabilities | Machining capabilities, machine tools, accuracy of execution. | Multi-axis CNC lathes; Advanced alloys & plastics; Tight tolerance machining | Ensures capability to produce complex, high-specification parts. |
| Quality Assurance | Inspecting to remove defects. | In-process inspection; Advanced metrology (CMM); Full Documentation (C of C) | It ensures the quality and prevents the chances of defect. |
| The Partnership Advantage | Collaboration for long-term success. | Proactive communication; DFM feedback; Supply chain integration | Drives innovation, reduces time-to-market, and optimizes total cost. |
LS Manufacturing redefines precision CNC turning by combining advanced technical capabilities with rigorous, data-driven process control. This ensures unmatched quality consistency for complex parts. Moving beyond a transactional relationship, our partnership model focuses on deep collaboration and proactive solutions, delivering not just components, but reliable performance and significant total cost of ownership advantages for our clients.
Why Trust This Guide? Practical Experience From LS Manufacturing Experts
Advice from someone who knows what they’re talking about – and has the experience Why this approach will work: This approach has been derived through experiences rather than just based upon theories. Every single conclusion drawn and provided throughout these pages in this document has, in fact, been embodied by us in our own personal experiences toward machining operational parts. It has provided us with success in over 50,000 custom parts and provided us with an understanding of what will and will not work in actual, real-world environments that parts such as stainless steel and titanium are typically placed within.
Our expertise and know-how have been derived within some of the toughest industries. Your system uptime could depend upon our ability to ensure proper thread accuracy within Aerospace parts, and our surface finishes provided for usage within Medical Implants could be critical in this product category. This represents and reflects the amount and level of expertise and knowledge that we have thus far obtained, referencing guidelines provided by those such as Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in guidelines based upon operational safety, and similar.
These best practices, in turn, continue to evolve through endless problem-solving within our shop floors and through our continued emphasis and attention toward efficiency and perfect, unimpeachable quality. Our practices and procedures have had to and will continue to be in compliance with tough guidelines, such as those based within environment channels in compliance with guidelines within US Environmental Protection Agency(US EPA) principles.
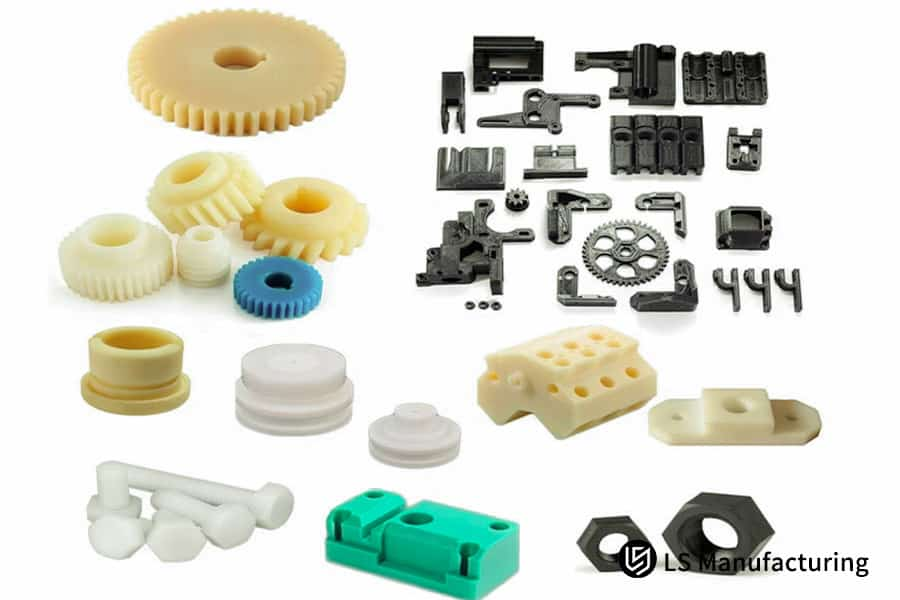

Figure 1: Range of precision CNC lathe-produced components by LS Manufacturing
How Does True Precision CNC Turning Service Surpass Ordinary Machining?
The difference from ordinary processing is fundamental. While standard machine shops focus primarily on making parts to a print, authentic precision CNC turning services are defined by a deeper commitment to engineering predictable outcomes. This involves implementing a rigorous, systematic methodology that actively controls every variable—from material integrity to toolpath optimization—throughout the manufacturing lifecycle. The ultimate goal is to guarantee not only dimensional conformance but also the functional performance, structural integrity, and long-term reliability of the critical component in its end-use application.
| Aspect | Ordinary Machining | True Precision Turning |
| Equipment & Accuracy | Average machines; expected general tolerances. | High-quality CNC lathes; accurate to sub. |
| Quality Control | Final inspection; defect sorting by reaction. | SPC; process control; defect prevention by anticipation. |
| Process & Documentation | Basic setup sheets; relies heavily on operators' experience. | Detailed control plans and FMEAs; completely documented process. |
| Outcome & Partnership | Transactional - outputs package printing elements. | Collaborative - risks are reduced and performance assured. |
The main differentiator is found within the total system as an entirety. Moreover, the fact is that high-quality turning machining manufacturers, such as LS Manufacturing, emphasize the importance of quality systems complemented with the finest machines. There is a shift within the manufacturing process of the plant from cost-effective to a source for differentiation, as well as an assured supply of parts and cost within the process.
What Are The Core Steps In The CNC Turning Process?
A successful CNC turning process is a meticulously planned and carefully orchestrated sequence, extending far beyond a basic set of machine operations. It is the deliberate, end-to-end integration of three critical, interconnected phases: comprehensive planning, controlled execution, and rigorous verification. This systematic discipline ensures the final component consistently meets its exacting design specifications. Therefore, the real and sustainable value of the process lies in the strategic, quality-driven choices implemented at each and every one of these decisive stages.
| Stage | Core Action | LS Manufacturing Value-Added Focus |
| Planning & Design Review | Part drawing analysis review. | Reactive & proactive comments on DFM (Design for Manufacturability). |
| CAM Programming & Setup | Machine tool path programming. | Effective CAM techniques and optimized tool path layouts that can lead to improved surface finishes, reduced processing time, and longer tool life. |
| First Article Inspection | Inspection first part verification. | Strict verification by CMM to have an overall digital documentation of its compliance to the 3D part model. |
| Production & In-Process Control | Implementation of actual production process start. | Active LS Manufacturing quality control process, with process checks and SPC to make sure that first and last items are of same quality. |
The absolute reliability of a mission-critical component is built and validated methodically, step by step. It is the unwavering attention to detail within each of the precision machining steps, combined with a true collaborative partnership that extends from design through to final manufacturing, which elevates the work from a simple process to an engineering achievement. It is precisely this integrated methodology and shared commitment to excellence that gives our partnership its profound and tangible meaning.
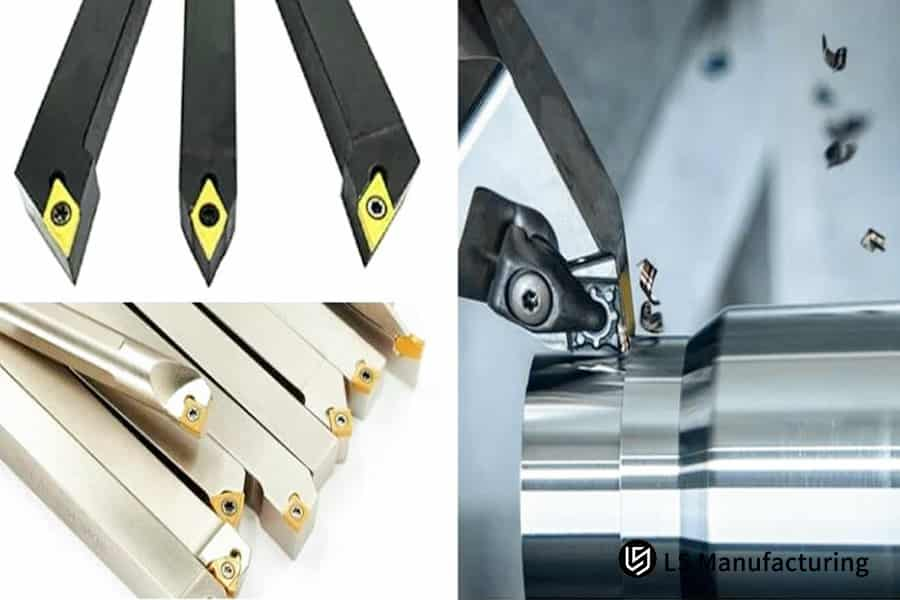

Figure 2: CNC turning tooling components and cutting process by LS Manufacturing
What Are The Key Advantages That Choosing Precision Turning Services Can Bring To Your OEM Projects?
The selection of the machining suppliers can greatly add to or just help improve the working of an organization. The greatest CNC turning benefits projects are maximized by undertaking work on these three key sectors that include project implementation time, capital investment, and project logistics. The three sectors have immense effects on the efficiency of an organization and can hence impact the profitability of projects.
- Reduced Total Cost of Ownership: The initial benefits of OEM project processing, which affects the user as well as the manufacturer, will be the minimized Total Cost of Ownership. Accuracy automatically reduces scrap and maximizes the assembly, which in turn reduces the returns, thereby resulting in reduced Total Cost of Ownership, which can be decreased by at least 15%.
- Enhanced Product Performance & Reliability: The precise parts have flawless functioning, which results in incredible performances of final products. The parts have a life span and function in an efficient system. This intrinsic value of choosing precision turning translates into a stronger brand reputation for quality and reduced warranty claims for your business.
- Supply Chain Simplification & Predictability: When one partners with a strong manufacturing partner, the job becomes much easier to exploit your own strengths as a business entity. They assist you in the simplification of your supply chain to source everything from their manufacturing partner. Neither is there any confusion regarding the technical communication nor uncertainty regarding the times of delivery.
In either scenario, the strategic value of choosing precision turning becomes self-evident. It dramatically changes the conversation from one centred on the actual price of an individual component to one of overall project merit. The overall project merit includes optimized cost effectiveness, best-in-class and assured quality, and improved and optimized agility within the supply chain.
What Are The Key Factors Affecting The Price Of Precision CNC Turning?
Understanding the factors affecting CNC turning prices is essential for accurate project budgeting. There are factors that you can take into consideration, which include part complexity, material, level of tolerance, as well as the level of manufacture. These are the individual factors that will determine the cost that has to be charged. Your design, as well as level of tolerance, determines an increase in the cost for custom parts.
Part Complexity & Setup
The initial and most significant precision CNC machining cost analysis factor is geometric complexity. Intricate features, multiple operations, and special tooling increase programming and setup time. A simple spacer and a multi-profile hydraulic fitting, even from the same material, have vastly different base costs due to this foundational setup requirement.
Material & Tolerances
The nature of the material chosen and its characteristics to be machinable will directly affect one of the most crucial factors in calculating the production cost. Furthermore, the tolerance levels in the dimensioning design chosen will carry an alarmingly massive and exaggerated influence in the cost calculation process for this product. Therefore, the existence and requirements for a tolerance factor will demand an exponentially higher attention magnitude concerning processing and technology for the value of ±0.0005 inches, as opposed to the value selection for the ±0.005 inches for the production of precise products.
Order Volume & Finishing
The custom turning parts pricing structure identifies order volume as the most significant cost driver. There is a higher proportion of the cost structure comprised of set-up for low-volume production and fixed cost amortization for high-volume production. Ancillary services such as anodizing, plating, and polish services can be considered value-added services that incur identifiable additional costs.
This means that for a complete precision machining cost analysis, there are four significant pillars that are taken into account, which are the complexity of parts, material, level of tolerance, and volume. The investment in the design and procurement of a part can thus be maximized to get the highest value for the machined item when there is complete knowledge of all the parameters associated factors affecting CNC turning prices.
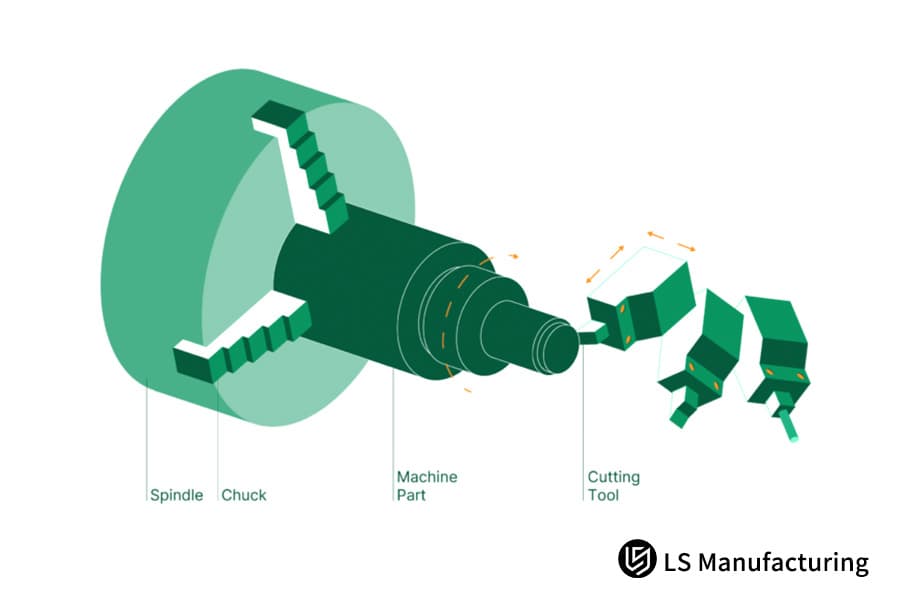
Figure 3: Core elements and procedures of the CNC turning process by LS Manufacturing
Medical Device Industry: Multi-Axis Precision Turning Of Implantable Titanium Alloy Bone Screws
The LS Manufacturing case study illustrates how our specific case history applies to very high mission-critical production for medical components. The case history describes how our reason for performing medical device parts processing resolved a significant production issue for a significant orthopedic device manufacturing company. This not only addressed their requirement for precise specifications, but they required a significant level of assurance in their supply chain.
Client Challenge
The critical requirement in this particular instance has been the mass production of bone screws from the titanium-alloy material F-136. There are also extremely critical requirements in this particular project pertaining to the threading accuracy in terms of microns, as well as the sterile packaging. All such activities performed by prevailing suppliers are creating critical compliance problems with the regulations of the Food & Drug Administration.
LS Manufacturing Solution
For this turning service, we utilized titanium alloy precision turning solutions. During the making of the product, we employed high-precision, Swiss-style turning machines and a micro-workholder custom-built to design. Manufacturing processes took place from machined product to packaged product in our Class 10,000 accredited cleanroom environment.
Results and Value
The outcome was a 99.9% first-pass yield rate, with the parts passing all dimensional and biocompatibility tests. This enabled a successful FDA audit and on-time product launch. While the initial CNC turning pricing was an investment, it eliminated costly delays and rework, establishing a foundation for a trusted, long-term strategic partnership.
This example clearly illustrates that the true value of medical device parts processing extends far beyond the initial per-unit manufacturing cost. It is, at its core, realized through a critical trio of deliverables: guaranteed micron-level precision, rigorous and documented process control, and an unwavering guarantee of regulatory compliance. Together, these elements ensure product integrity, mitigate risk, and transform a production requirement into a source of sustainable competitive advantage.
Make LS manufacturing turning a core competitive advantage for you. Contact us today for professional solutions to accelerate project success.
Why Can LS Manufacturing Be Your Reliable Precision Turning Supplier?
What a top CNC turning manufacturer does, instead, is more than the provision of parts; such a supplier provides a guarantee, alliance, and an overall system turning their designs into a guarantee of performance. This has come about because of the integration of their technology, precision, and services delivery that borders on industry best practices.
- Technical Excellence: The LS Manufacturing's manufacturing strength include highly advanced multi-axis turn mill centers with complete closed-loop control systems. These enable highly accurate machining operations to be completed in a single operation in order to ensure results that distinguish top CNC turning manufacturers. This will ensure that from around the world, the best and the most qualified people are selected.
- Certified Quality Assurance: Our commitment to reliability is enforced by a robust quality system certified to ISO 9001:2015 and IATF 16949, supported by comprehensive in-house metrology. This process-driven approach ensures rigorous documentation, traceability, and consistent compliance with your most demanding specifications, delivering peace of mind with every order.
- Deep Engineering Partnership: Apart from just the machines themselves, we provide access to technical expertise through our application engineering team. Strong material and process capabilities of our application engineering team enable proactive Design for Manufacturability (DFM), which optimizes your components right from the start of a project lifecycle.
- Project-Centric Collaboration: We are your solution partners, not just vendors. On each and every client project, we assign them an exclusive contact person and maintain an aggressive project management approach that ensures seamless communication and predictability in collaborative problem-solving issues throughout the whole manufacturing process-from prototype development to mass production.
First and foremost, our particular strength lies in utilizing all the pillars for technical excellence, certified quality, deep engineering, and client partnership. This is what makes LS Manufacturing different: it's wholesome, making it a reliable precision turning supplier who takes the pain not only to deliver the product but also expertise and assurance for your success.
How Can Your Design Reduce Turning Costs Through DFM Optimization?
An effective design is the initial and most impactful factor in managing production costs. Even minor optimizations in design concepts can significantly improve manufacturability, reduce cycle time, and lower costs while maintaining or enhancing reliability and full functionality. A well-structured turning machining design guide serves as an essential roadmap for this process, providing clear principles to harmonize part performance with efficient, cost-effective manufacturing from the very beginning.
Optimizing Design Elements for Efficiency
A key aspect of DFM optimization to reduce costs involves standardizing features like chamfer dimensions and radii, which allows for the use of common, in-stock tooling. Likewise, simplifying geometries by avoiding overly deep, small-diameter holes or extremely thin walls that are prone to vibration can drastically improve process stability, cutting time, and first-pass yield.
Applying Tolerances Strategically
Among all the designs mentioned in the concept of the Digital Factory Model, the most significant is the application of tolerance. In order to improve the performance of the product and eliminate the excess removal of material in the process of machining, the designer then employs a tight CNC turning tolerance in the non-critical areas together with the modification of the tolerance on the non-critical dimension. Therefore, the effect of this process is the time saved both in machining and in the inspection process without affecting the total cost.
Enhancing Setup and Tooling Efficiency
Optimization is also applicable as an aid in the harmonization of processes. Optimal design may also involve the application of symmetrical design features and standard thread sizes. By reducing the complexity of processes that involve multiple uses of the same tool and geometries that involve breakable tooling, machined cycles may be optimized.
In an effort to assist in implementing these guiding principles, we would be able to provide our free DFM analysis service. In this initial stage of your project cycle, we would be able to provide expert guidance in regard to your particular design and suggest in which manner your expenses could be decreased or in which manner qualified risk could be mitigated through this technology.
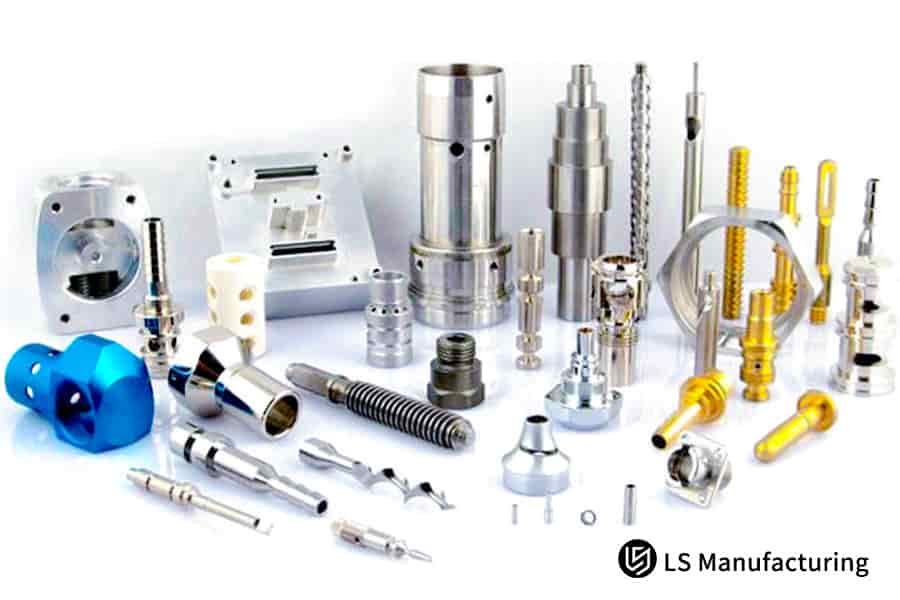

Figure 4: Product array of CNC-turned metal components and end uses by LS Manufacturing
How To Obtain An Accurate Quote From LS Manufacturing And Initiate Cooperation?
Establishing a successful and lasting manufacturing partnership should be built upon a clear, transparent, and easy-to-follow procedural framework. The LS Manufacturing inquiry process is designed with this principle at its core. From the initial engagement, we collaborate closely with you to define specifications, align on expectations, and outline a precise roadmap. This ensures that every step required to move your project from concept to finished product is clearly understood from the very beginning, enabling a swift, efficient, and predictable journey to completion.
- Submit Your Design for Review: The journey to get an accurate quote begins when you share your part drawings or 3D models along with key specifications (material, quantity, application). This provides our engineering team with the complete information needed to conduct a thorough preliminary assessment for your project’s feasibility and initial scope.
- Receive DFM Feedback & Formal Quotation: Within 24 hours, an in-depth proposal will be received. This process goes further than simply providing pricing, incorporating completely free DFM analysis recommendations to guarantee that the part has been optimized within manufacturability, performance, as well as cost. This step within the process allows what could be simply a quotation to actually plan on what both sides agree on what will be the next step.
- Confirm Order & Production Scheduling: Once you accept a quote that we have offered you, we will email you a formal purchase order confirmation and then immediately enter your project into our production schedule. This way, only one project coordinator will contact you regarding project updates and project timing to initiate a initiate CNC turning collaboration.
- First Article Approval & Full Production: We begin by producing and inspecting the First Article for you. We will issue an inspection report for your review and approval. After your inspection and approval of our First Article, which confirms that it meets your specifications, we can proceed to your full production.
Our goal is to establish the LS Manufacturing inquiry process as an industry benchmark for both clarity and partnership. We are committed to providing the technical expertise, full transparency, and proactive communication needed to seamlessly initiate CNC turning collaboration. From your initial file upload to the final on-time delivery, this guided and supportive experience builds the confidence necessary to ensure the complete success of your precision manufacturing project.
FAQs
1. To what degree of accuracy are you willing to compromise in this particular case?
The standard precision for precision turning that we provide is a tolerance level of ±0.01mm. While using multi-axis composite turning machines, along with temperature compensation technology, we are capable of providing ultra-precision levels for the functional dimension tolerance of either ±0.005mm or better, as well as reporting for the entire process.
2. Prototyping on a small scale and mass production?
Our flexible production systems also hold the capability of production of prototypes and large productions of tens of thousands of pieces. With the aid of an intelligent scheduling system and collaboration of different production lines, we also hold the capability of starting the process of production of prototypes within 24 hours and maintaining the stability of production capacity of large productions.
3. Does the quote include all costs? Are there hidden charges?
In our quote, there will always be a transparent cost structure that will comprise material cost, processing cost, normal test cost, and packaging cost. However, for any special processing need, special test need, or any special packaging need, there will be a separate detailed quotation that will be confirmed in writing without any surprise costs.
4. How can security and intellectual property rights in my design be protected?
We offer a confidentiality service in three levels. First, we sign a confidentiality agreement for business. Second, we make use of an extremely encrypted file transferring method, which is widely used in the military. Third, we apply hierarchical control. The files will be destroyed after transferring.
5. May I inquire as to whether the inspection of the first piece has yet been concluded?
We give a comprehensive report on dimensional inspection based on an inspection done by using a coordinate measurement machine. Moreover, if required, an inspection review will be initiated by the quality team within an overall time of 4 hours through online video retesting and comparisons based on 100% consensus on acceptance standards.
6. What is the normal cycle of production, and how can this cycle be accelerated?
The average turn-around time for such cases would be around 10 to 15 working days. In cases where urgent turn-around times may be required, for our firm, we would have our green expedition process. This would help us in accomplishing any job within 72 hours by focusing on time schedules and determining shorter process paths. Tailor-made solutions would also be devised by project managers.
7. What material certifications and quality documents do you provide?
We provide a complete quality traceability documentation package, including original manufacturer's quality certificates for raw materials, metallographic analysis reports, first-article FAIR reports, process SPC data, and final inspection reports, fully meeting the certification requirements of industries such as aerospace and medical.
8. What if a part, after being processed by you, encounters a problem during our assembly?
We promise to activate a rapid response mechanism, with our technical team intervening within 8 hours for analysis. If the issue is confirmed to be process-related, we will immediately initiate a priority rework process, bearing the relevant logistics and rework costs, and providing a root cause analysis report to ensure a closed-loop resolution of the problem.
Summary
For a successful OEM project, it can be achieved only by selecting a trustworthy, communicating, and reliable supplier of precision turning. LS Manufacturing, with its prime focus on process, value, and delivery, has made its stance as a trustworthy source for industry majors, as it has been noted in the case study, “Medical Device Industry: Multi-Axis Precision Turning of Implantable Titanium Alloy Bone Screws.”
Similarly, your project too can get the best aid from the industry. Click “Get My Free Quote and DFM Analysis” today, and within 24 hours, the top-class aid will be provided by the experts in our team.
Get a personalized quote now and unlock the manufacturing potential of your products. Click to contact us!

📞Tel: +86 185 6675 9667
📧Email: info@longshengmfg.com
🌐Website:https://lsrpf.com/
Disclaimer
The contents of this page are for informational purposes only. LS Manufacturing services There are no representations or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or validity of the information. It should not be inferred that a third-party supplier or manufacturer will provide performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design characteristics, material quality and type or workmanship through the LS Manufacturing network. It's the buyer's responsibility. Require parts quotation Identify specific requirements for these sections.Please contact us for more information.
LS Manufacturing Team
LS Manufacturing is an industry-leading company. Focus on custom manufacturing solutions. We have over 20 years of experience with over 5,000 customers, and we focus on high precision CNC machining, Sheet metal manufacturing, 3D printing, Injection molding. Metal stamping,and other one-stop manufacturing services.
Our factory is equipped with over 100 state-of-the-art 5-axis machining centers, ISO 9001:2015 certified. We provide fast, efficient and high-quality manufacturing solutions to customers in more than 150 countries around the world. Whether it is small volume production or large-scale customization, we can meet your needs with the fastest delivery within 24 hours. choose LS Manufacturing. This means selection efficiency, quality and professionalism.
To learn more, visit our website:www.lsrpf.com.